How Symmetry Shapes Nature's Laws (2 min)
Kaplan_Symmetry.mp4
 What is symmetry?
In physics, symmetry refers to a system’s invariance under
transformations, such as shifts in space, time, or internal
properties. Common symmetries include translational
(unchanged when moved), rotational (unchanged when rotated),
and time reversal. Symmetry often leads to conservation
laws—Noether’s theorem connects symmetries with conserved
quantities like energy and momentum.
Internal symmetries, like gauge symmetries, play a key role
in particle physics. Symmetry breaking explains phenomena
like phase transitions. Symmetry underpins the laws of
physics and is central to theories such as quantum mechanics
and general relativity.
Conservation Laws
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conservation_law
In physics, a conservation law states that a particular
measurable property of an isolated physical system does not
change as the system evolves over time. Exact conservation
laws include conservation of mass-energy, conservation of
linear momentum, conservation of angular momentum, and
conservation of electric charge.
A partial listing of physical conservation equations due to
symmetry that are said to be exact laws, or more precisely
have never been proven to be violated:
What is symmetry?
In physics, symmetry refers to a system’s invariance under
transformations, such as shifts in space, time, or internal
properties. Common symmetries include translational
(unchanged when moved), rotational (unchanged when rotated),
and time reversal. Symmetry often leads to conservation
laws—Noether’s theorem connects symmetries with conserved
quantities like energy and momentum.
Internal symmetries, like gauge symmetries, play a key role
in particle physics. Symmetry breaking explains phenomena
like phase transitions. Symmetry underpins the laws of
physics and is central to theories such as quantum mechanics
and general relativity.
Conservation Laws
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conservation_law
In physics, a conservation law states that a particular
measurable property of an isolated physical system does not
change as the system evolves over time. Exact conservation
laws include conservation of mass-energy, conservation of
linear momentum, conservation of angular momentum, and
conservation of electric charge.
A partial listing of physical conservation equations due to
symmetry that are said to be exact laws, or more precisely
have never been proven to be violated:
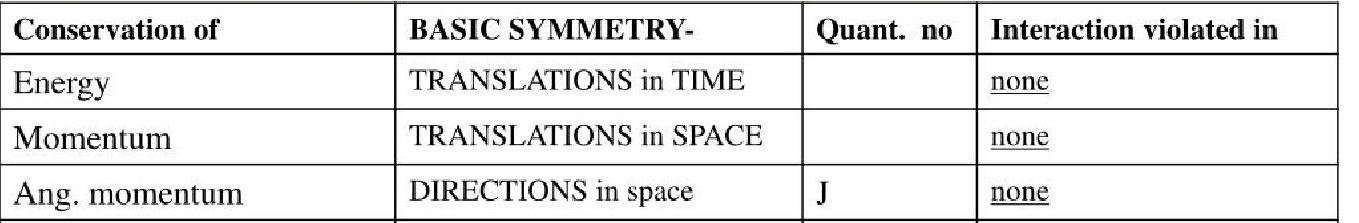
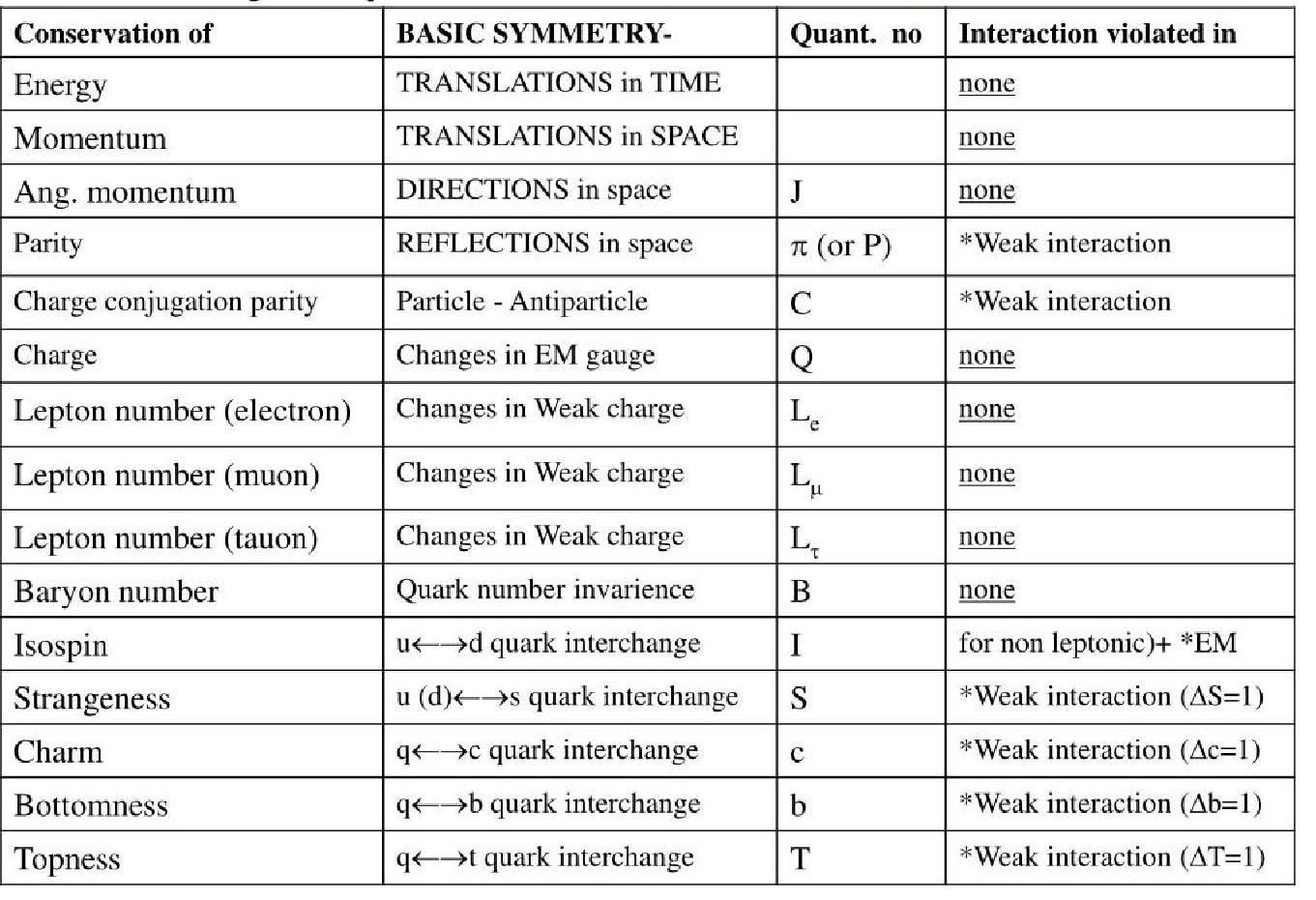 There are also many approximate conservation laws, which
apply to such quantities as mass, parity, lepton number,
baryon number, strangeness, hypercharge, etc. These
quantities are conserved in certain classes of physics
processes, but not in all.
Noether's Theorem and The Symmetries of Reality 9+ min
Noethers-Theorem.mp4
Noether's theorem states that every continuous symmetry of
the action of a physical system with conservative forces has
a corresponding conservation law. This is the first of two
theorems (see Noether's second theorem) published by
mathematician Emmy Noether in 1918. The action of a physical
system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function,
from which the system's behavior can be determined by the
principle of least action. This theorem only applies to
continuous and smooth symmetries of physical space.
Noether's theorem is used in theoretical physics and the
calculus of variations. It reveals the fundamental relation
between the symmetries of a physical system and the
conservation laws.
There are also many approximate conservation laws, which
apply to such quantities as mass, parity, lepton number,
baryon number, strangeness, hypercharge, etc. These
quantities are conserved in certain classes of physics
processes, but not in all.
Noether's Theorem and The Symmetries of Reality 9+ min
Noethers-Theorem.mp4
Noether's theorem states that every continuous symmetry of
the action of a physical system with conservative forces has
a corresponding conservation law. This is the first of two
theorems (see Noether's second theorem) published by
mathematician Emmy Noether in 1918. The action of a physical
system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function,
from which the system's behavior can be determined by the
principle of least action. This theorem only applies to
continuous and smooth symmetries of physical space.
Noether's theorem is used in theoretical physics and the
calculus of variations. It reveals the fundamental relation
between the symmetries of a physical system and the
conservation laws.
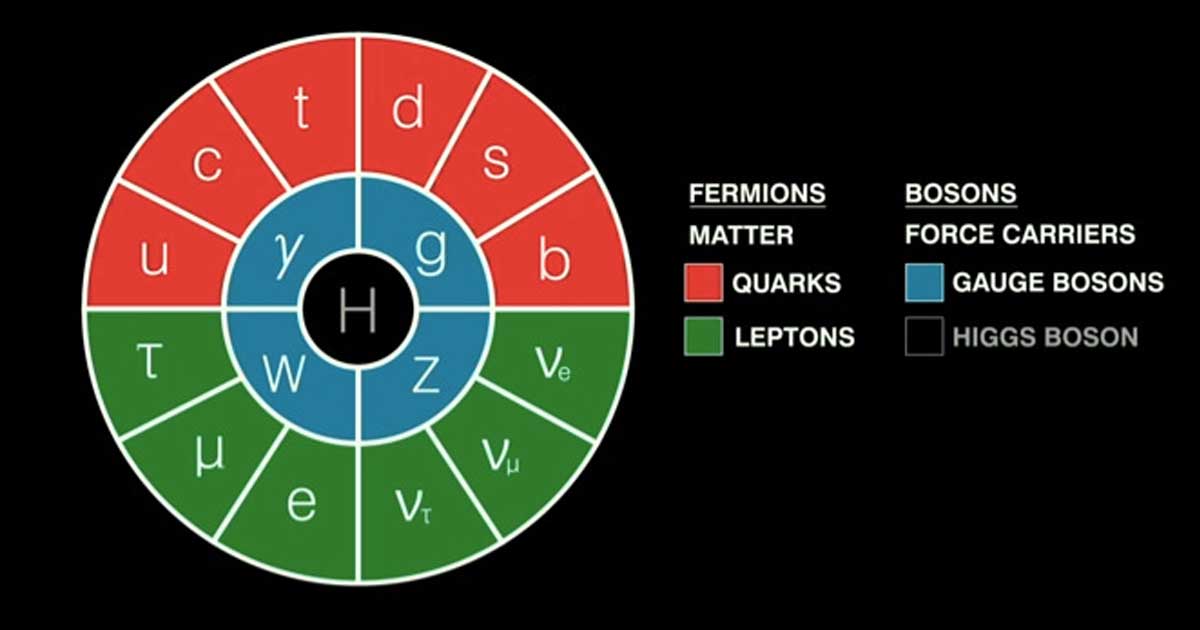 What's the relationship between symmetry and invariant properties?
Symmetry-Invariant_Properties.pdf
Key Insights:
- Symmetry is about transformations that leave something
unchanged.
- Invariance refers to the property or quantity that remains
unchanged under these transformations.
- Symmetry gives rise to invariant properties, linking the
two concepts in various scientific and mathematical
contexts.
How does symmetry create conservation laws?
Symmetry-Conservation_Laws.pdf
Summary
- Symmetry transformations (like shifts in space, time, or
rotation) leave the laws of physics unchanged.
- Noether’s Theorem tells us that each symmetry corresponds
to a conserved quantity:
- Space translation symmetry → Conservation of linear
momentum
- Time translation symmetry → Conservation of energy
- Rotation symmetry → Conservation of angular momentum
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES
By A. Einstein
June 30, 1905
http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/specrel.pdf
Beautiful, Simple and Profound - Final Development and Testing GR
Einstein_Documentary.mp4
49:40 --> 56:50 (7 min)
1:13:50 --> 1:29 (15 min)
What is symmetry's role in General Relativity?
Symmetry-GR.pdf
Symmetry in general relativity manifests in the invariance
of physical laws across spacetime, the existence of
conserved quantities due to Noether’s theorem, and the form
of specific spacetime solutions that exhibit various types
of symmetry (such as spherical or rotational). Symmetry
provides a guiding principle in both formulating GR and
understanding the structure of the universe.
What's the relationship between symmetry and invariant properties?
Symmetry-Invariant_Properties.pdf
Key Insights:
- Symmetry is about transformations that leave something
unchanged.
- Invariance refers to the property or quantity that remains
unchanged under these transformations.
- Symmetry gives rise to invariant properties, linking the
two concepts in various scientific and mathematical
contexts.
How does symmetry create conservation laws?
Symmetry-Conservation_Laws.pdf
Summary
- Symmetry transformations (like shifts in space, time, or
rotation) leave the laws of physics unchanged.
- Noether’s Theorem tells us that each symmetry corresponds
to a conserved quantity:
- Space translation symmetry → Conservation of linear
momentum
- Time translation symmetry → Conservation of energy
- Rotation symmetry → Conservation of angular momentum
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES
By A. Einstein
June 30, 1905
http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/specrel.pdf
Beautiful, Simple and Profound - Final Development and Testing GR
Einstein_Documentary.mp4
49:40 --> 56:50 (7 min)
1:13:50 --> 1:29 (15 min)
What is symmetry's role in General Relativity?
Symmetry-GR.pdf
Symmetry in general relativity manifests in the invariance
of physical laws across spacetime, the existence of
conserved quantities due to Noether’s theorem, and the form
of specific spacetime solutions that exhibit various types
of symmetry (such as spherical or rotational). Symmetry
provides a guiding principle in both formulating GR and
understanding the structure of the universe.
Science News Media
The Year in Mathematics (2024)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lwVSeXswWZY
Latest Science (all sciences)
http://edu-observatory.org/media/Science/index.html#LATEST
ChatGPT
https://chat.openai.com/chat
DuckDuckGo
What is symmetry? In physics, symmetry refers to a system’s invariance under transformations, such as shifts in space, time, or internal properties. Common symmetries include translational (unchanged when moved), rotational (unchanged when rotated), and time reversal. Symmetry often leads to conservation laws—Noether’s theorem connects symmetries with conserved quantities like energy and momentum. Internal symmetries, like gauge symmetries, play a key role in particle physics. Symmetry breaking explains phenomena like phase transitions. Symmetry underpins the laws of physics and is central to theories such as quantum mechanics and general relativity. Conservation Laws https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conservation_law In physics, a conservation law states that a particular measurable property of an isolated physical system does not change as the system evolves over time. Exact conservation laws include conservation of mass-energy, conservation of linear momentum, conservation of angular momentum, and conservation of electric charge. A partial listing of physical conservation equations due to symmetry that are said to be exact laws, or more precisely have never been proven to be violated:

There are also many approximate conservation laws, which apply to such quantities as mass, parity, lepton number, baryon number, strangeness, hypercharge, etc. These quantities are conserved in certain classes of physics processes, but not in all. Noether's Theorem and The Symmetries of Reality 9+ min Noethers-Theorem.mp4 Noether's theorem states that every continuous symmetry of the action of a physical system with conservative forces has a corresponding conservation law. This is the first of two theorems (see Noether's second theorem) published by mathematician Emmy Noether in 1918. The action of a physical system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function, from which the system's behavior can be determined by the principle of least action. This theorem only applies to continuous and smooth symmetries of physical space. Noether's theorem is used in theoretical physics and the calculus of variations. It reveals the fundamental relation between the symmetries of a physical system and the conservation laws.
What's the relationship between symmetry and invariant properties? Symmetry-Invariant_Properties.pdf Key Insights: - Symmetry is about transformations that leave something unchanged. - Invariance refers to the property or quantity that remains unchanged under these transformations. - Symmetry gives rise to invariant properties, linking the two concepts in various scientific and mathematical contexts. How does symmetry create conservation laws? Symmetry-Conservation_Laws.pdf Summary - Symmetry transformations (like shifts in space, time, or rotation) leave the laws of physics unchanged. - Noether’s Theorem tells us that each symmetry corresponds to a conserved quantity: - Space translation symmetry → Conservation of linear momentum - Time translation symmetry → Conservation of energy - Rotation symmetry → Conservation of angular momentum ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. Einstein June 30, 1905 http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/specrel.pdf Beautiful, Simple and Profound - Final Development and Testing GR Einstein_Documentary.mp4 49:40 --> 56:50 (7 min) 1:13:50 --> 1:29 (15 min) What is symmetry's role in General Relativity? Symmetry-GR.pdf Symmetry in general relativity manifests in the invariance of physical laws across spacetime, the existence of conserved quantities due to Noether’s theorem, and the form of specific spacetime solutions that exhibit various types of symmetry (such as spherical or rotational). Symmetry provides a guiding principle in both formulating GR and understanding the structure of the universe.