FEYNMAN LECTURES ON PHYSICS
https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu
Feynman Lecture No. 1 - Atoms in Motion
https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/I_01.html
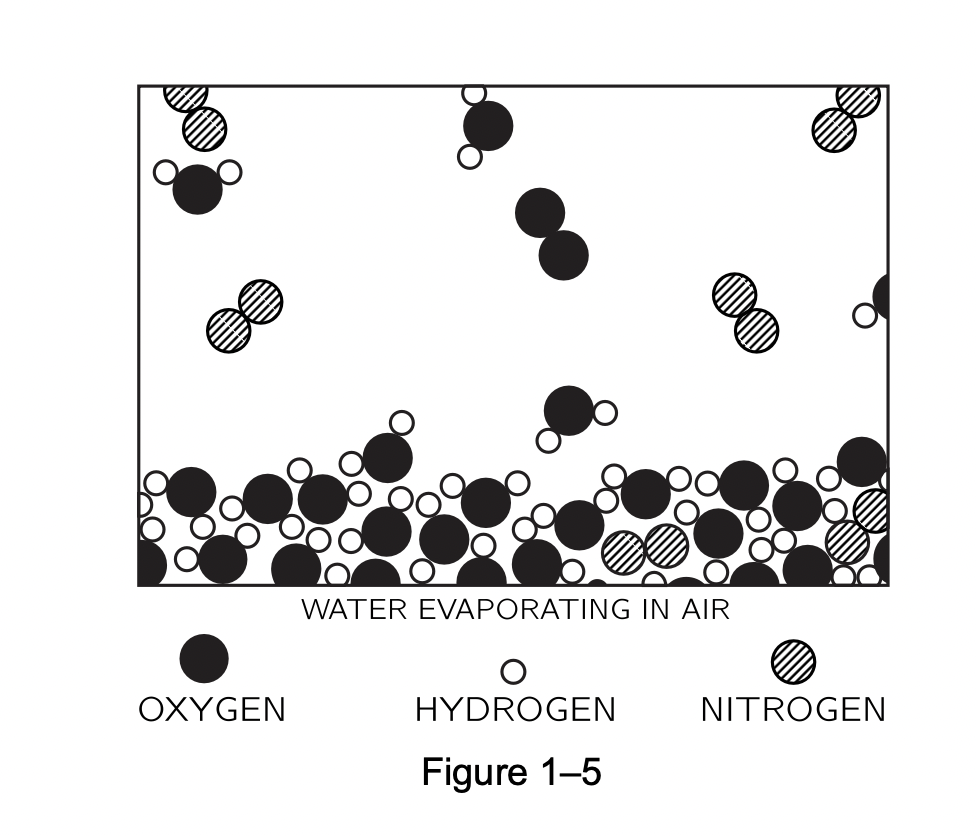
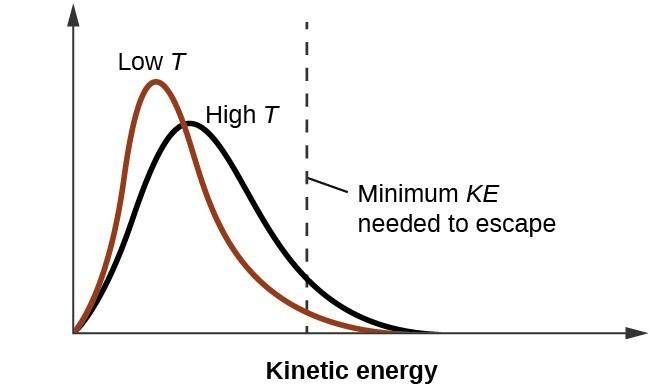 Attractive intermolecular forces are categorized into the
following types:
o Hydrogen bonding
o Ion-dipole forces and ion-induced dipole forces
o Van der Waals forces
Two important principles:
1. Evaporation: Cools the Water ==> Warms the Atmosphere
2. No evaporation takes place when the relative humidity
of the air is 100 percent (saturated)
Attractive intermolecular forces are categorized into the
following types:
o Hydrogen bonding
o Ion-dipole forces and ion-induced dipole forces
o Van der Waals forces
Two important principles:
1. Evaporation: Cools the Water ==> Warms the Atmosphere
2. No evaporation takes place when the relative humidity
of the air is 100 percent (saturated)
 EXTREMELY HOT, HUMID WEATHER COULD KILL A PERSON FAR MORE
EASILY THAN WE THOUGHT
https://www.sciencealert.com/human-survival-in-hot-and-humid-conditions-is
https://www.sciencealert.com/future-heat-waves-are-coming-and-these-countries-are-most-at-risk
The human body might not cope with nearly as much heat and
humidity as theory predicts.
One of the first studies to directly assess humid heat
stress among young people has found that when humidity is at
an absolute max, the upper limit of human adaptability is
just 31°C (87°F).
EXTREMELY HOT, HUMID WEATHER COULD KILL A PERSON FAR MORE
EASILY THAN WE THOUGHT
https://www.sciencealert.com/human-survival-in-hot-and-humid-conditions-is
https://www.sciencealert.com/future-heat-waves-are-coming-and-these-countries-are-most-at-risk
The human body might not cope with nearly as much heat and
humidity as theory predicts.
One of the first studies to directly assess humid heat
stress among young people has found that when humidity is at
an absolute max, the upper limit of human adaptability is
just 31°C (87°F).
SOME DEFINITIONS
 Heat Wave
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_wave
https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/what-causes-a-heat-wave.html
What Causes A Heat Wave?
A heat wave is formed when the upper atmosphere contains
high pressure which makes it stationary over a region. This
stationary mass of air can remain stagnant for several days
and weeks, trapping more heat and reducing convection
currents. As a result, there is accumulated heat and high
humidity without any precipitation or rainfall. This creates
the abnormally high temperatures. Heat waves are quite
common during the summer season, from May to November in the
northern hemisphere.
The high pressure forces air to sink to the surface of the
land and acts as a barrier for heat to rise. This blankets
the earth surface and traps all elements of weather without
allowing them to escape.
The Hazards Of A Heat Wave
A heat wave is potentially more dangerous than other natural
events such as hurricanes, lightning, and tornadoes. Aside
from causing uncomfortably high temperatures, heat waves can
result in heat illness, poor air quality, wildfires, and
drought.
Severe heat waves have caused catastrophic crop failures,
thousands of deaths from hyperthermia, and widespread power
outages due to increased use of air conditioning. A heat
wave is considered extreme weather that can be a natural
disaster, and a danger because heat and sunlight may
overheat the human body. Heat waves can usually be detected
using forecasting instruments so that a warning call can be
issued.
Heat Exhaustion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_exhaustion
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/symptoms-causes/syc-20373250
Heat exhaustion is a severe form of heat illness. It is a
medical emergency. Heat exhaustion is caused by the loss of
water and electrolytes through sweating.
Heat Stroke
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_stroke
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20353581
Heatstroke is a condition caused by your body overheating,
usually as a result of prolonged exposure to or physical
exertion in high temperatures. This most serious form of
heat injury, heatstroke, can occur if your body temperature
rises to 104°F (40°C) or higher. The condition is most
common in the summer months and heat waves.
Heatstroke requires emergency treatment. Untreated
heatstroke can quickly damage your brain, heart, kidneys and
muscles. The damage worsens the longer treatment is delayed,
increasing your risk of serious complications or death.
Heat Wave
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_wave
https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/what-causes-a-heat-wave.html
What Causes A Heat Wave?
A heat wave is formed when the upper atmosphere contains
high pressure which makes it stationary over a region. This
stationary mass of air can remain stagnant for several days
and weeks, trapping more heat and reducing convection
currents. As a result, there is accumulated heat and high
humidity without any precipitation or rainfall. This creates
the abnormally high temperatures. Heat waves are quite
common during the summer season, from May to November in the
northern hemisphere.
The high pressure forces air to sink to the surface of the
land and acts as a barrier for heat to rise. This blankets
the earth surface and traps all elements of weather without
allowing them to escape.
The Hazards Of A Heat Wave
A heat wave is potentially more dangerous than other natural
events such as hurricanes, lightning, and tornadoes. Aside
from causing uncomfortably high temperatures, heat waves can
result in heat illness, poor air quality, wildfires, and
drought.
Severe heat waves have caused catastrophic crop failures,
thousands of deaths from hyperthermia, and widespread power
outages due to increased use of air conditioning. A heat
wave is considered extreme weather that can be a natural
disaster, and a danger because heat and sunlight may
overheat the human body. Heat waves can usually be detected
using forecasting instruments so that a warning call can be
issued.
Heat Exhaustion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_exhaustion
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/symptoms-causes/syc-20373250
Heat exhaustion is a severe form of heat illness. It is a
medical emergency. Heat exhaustion is caused by the loss of
water and electrolytes through sweating.
Heat Stroke
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_stroke
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20353581
Heatstroke is a condition caused by your body overheating,
usually as a result of prolonged exposure to or physical
exertion in high temperatures. This most serious form of
heat injury, heatstroke, can occur if your body temperature
rises to 104°F (40°C) or higher. The condition is most
common in the summer months and heat waves.
Heatstroke requires emergency treatment. Untreated
heatstroke can quickly damage your brain, heart, kidneys and
muscles. The damage worsens the longer treatment is delayed,
increasing your risk of serious complications or death.
HOW TO STAY SAFE DURING EXCESSIVE HEAT EVENTS (from
the National Weather Service)
https://www.weather.gov/safety/heat-during



 Mayo Clinic - Heat Exhaustion
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373253
Mayo Clinic - Heat Exhaustion
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373253

 Mayo Clinic - Heat Stroke
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20353581
Mayo Clinic - Heat Stroke
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20353581

COOLING
Should You Wipe Off Your Sweat (4- min)
Should_You_Wipe_Off_Your_Sweat.mp4
Heat Stress Hydration
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/mining/UserFiles/works/pdfs/2017-126.pdf
Drinking enough fluids is one of the most important things
you can do to prevent heat illness. Water is generally
sufficient for hydration.
Water will almost always maintain hydration during work in
the heat, as long as you eat regular meals to replace salt
lost in sweat.
Scientific American Podcast: the smart way to stay cool
https://www.scientificamerican.com/podcast/episode/how-to-cool-down-fast-in-summer-heat/
For a shortcut to relief in hot weather, immerse your hands
in cool water, biologist Craig Heller tells a Scientific
American podcast. The hairless skin on our palms, soles and
upper face contain special blood vessels - arteriovenous
anastomoses (AVAs) - that offer a more direct connection to
the core of the body, bypassing the delicate capillaries.
Gently cooling this skin helps you to chill out fast — but
avoid freezing-cold water, which will cause the AVAs to slam
closed. What not to do: use ice or a wet towel on the back
of your neck. You'll be misleading your brain's thermostat,
which uses the temperature of this area to trigger your
body’s natural cooling methods.
Opinion: Life hacks from India on how to stay cool (without
an air conditioner)
https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2022/08/02/1114354904/opinion-life-hacks-from-india-on-how-to-stay-cool-without-an-air-conditioner
 How to protect the people you care about from extreme heat
https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2022/08/04/1114996392/how-to-protect-the-people-you-care-about-from-extreme-heat
https://www.npr.org/2022/07/01/1109415329/how-to-stay-safe-and-cool-in-extreme-heat
How to protect the people you care about from extreme heat
https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2022/08/04/1114996392/how-to-protect-the-people-you-care-about-from-extreme-heat
https://www.npr.org/2022/07/01/1109415329/how-to-stay-safe-and-cool-in-extreme-heat
 How to Keep Cool When You Don't Have Air Conditioning at Home
https://www.ecowatch.com/staying-cool-tips-heat-climate-change.html
How to Keep Cool When You Don't Have Air Conditioning at Home
https://www.ecowatch.com/staying-cool-tips-heat-climate-change.html
 Evaporative Cooling (won't work in high humidity)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Passive_cooling
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evaporative_cooler
Cooling air temperatures that can be achieved by a direct
evaporative cooler at various outdoor conditions.
Evaporative Cooling (won't work in high humidity)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Passive_cooling
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evaporative_cooler
Cooling air temperatures that can be achieved by a direct
evaporative cooler at various outdoor conditions.
 IMPORTANT: If power fails, there is no air conditioning, no
fans, water may become scarce or may not be cool enough to
cool your body. The only thing that can cool you is something
colder than the human body, preferably cooler than ~84°F.
Water running through underground pipes will tend to be cooled
(or heated) to the subsurface soil temperature. These soil
depth temperatures (below) are updated daily.
Soil Temperatures (US) Often Affects Tap Water Temperature
https://www.greencastonline.com/tools/soil-temperature
IMPORTANT: If power fails, there is no air conditioning, no
fans, water may become scarce or may not be cool enough to
cool your body. The only thing that can cool you is something
colder than the human body, preferably cooler than ~84°F.
Water running through underground pipes will tend to be cooled
(or heated) to the subsurface soil temperature. These soil
depth temperatures (below) are updated daily.
Soil Temperatures (US) Often Affects Tap Water Temperature
https://www.greencastonline.com/tools/soil-temperature
WATCHES, WARNINGS OR ADVISORIES
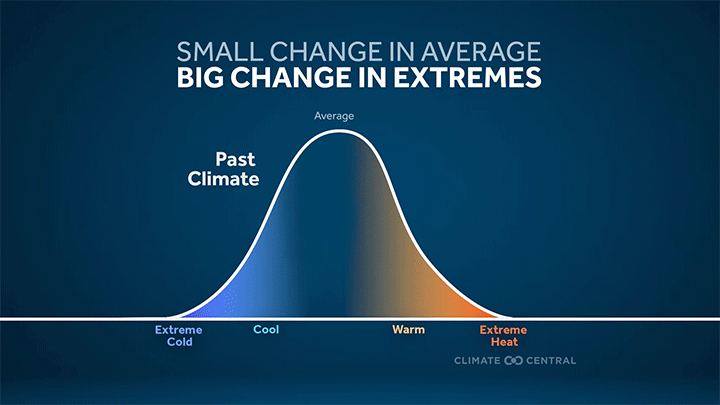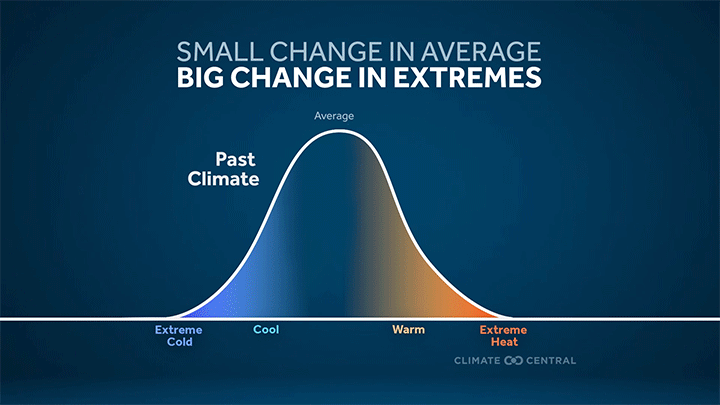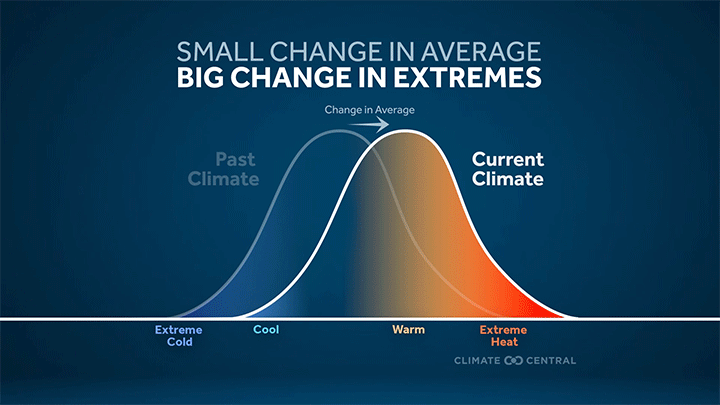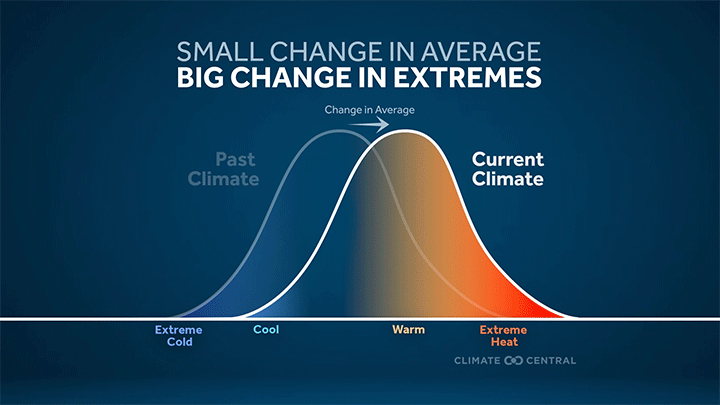 Graphic
Watches, Warnings or Advisories (CONUS)
https://www.weather.gov
Watches, Warnings or Advisories (Iowa)
https://www.weather.gov/dmx/
Text
Watches, Warnings or Advisories for the United States
https://alerts.weather.gov/cap/us.php?x=1
Watches, Warnings or Advisories by State
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/HEAT/warn_by_state.html
Watches and Warnings (Iowa)
https://alerts.weather.gov/cap/ia.php?x=1
HeatRisk Advisory Watch Warning MesoscaleAnalysis AQI Drought Risk
Graphic
Watches, Warnings or Advisories (CONUS)
https://www.weather.gov
Watches, Warnings or Advisories (Iowa)
https://www.weather.gov/dmx/
Text
Watches, Warnings or Advisories for the United States
https://alerts.weather.gov/cap/us.php?x=1
Watches, Warnings or Advisories by State
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/HEAT/warn_by_state.html
Watches and Warnings (Iowa)
https://alerts.weather.gov/cap/ia.php?x=1
HeatRisk Advisory Watch Warning MesoscaleAnalysis AQI Drought Risk
 Air Sea HeatIndexForecast Check IA Ames Watch Warning Outages
Air Sea HeatIndexForecast Check IA Ames Watch Warning Outages
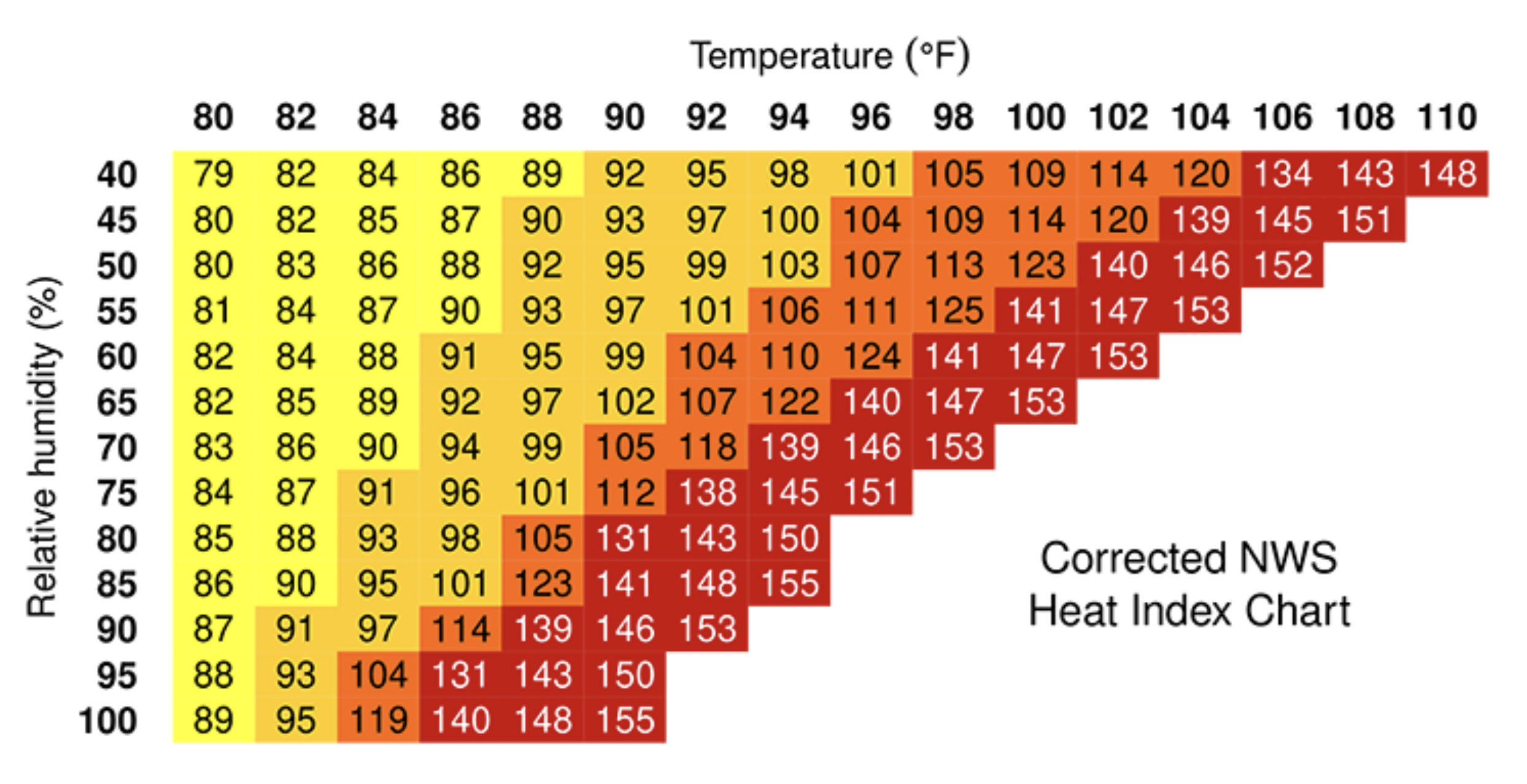 IMPORTANT: One of the reasons heat can be so dangerous is
because people don't take the risk seriously.
It surprises many people to learn that the heat index values
in the chart above are for shady locations. If you are
exposed to direct sunlight, the heat index value can be
increased by up to 14°F. Heat indices meeting or exceeding
103°F can lead to dangerous heat disorders with prolonged
exposure and/or physical activity in the heat.
IMPORTANT: One of the reasons heat can be so dangerous is
because people don't take the risk seriously.
It surprises many people to learn that the heat index values
in the chart above are for shady locations. If you are
exposed to direct sunlight, the heat index value can be
increased by up to 14°F. Heat indices meeting or exceeding
103°F can lead to dangerous heat disorders with prolonged
exposure and/or physical activity in the heat.
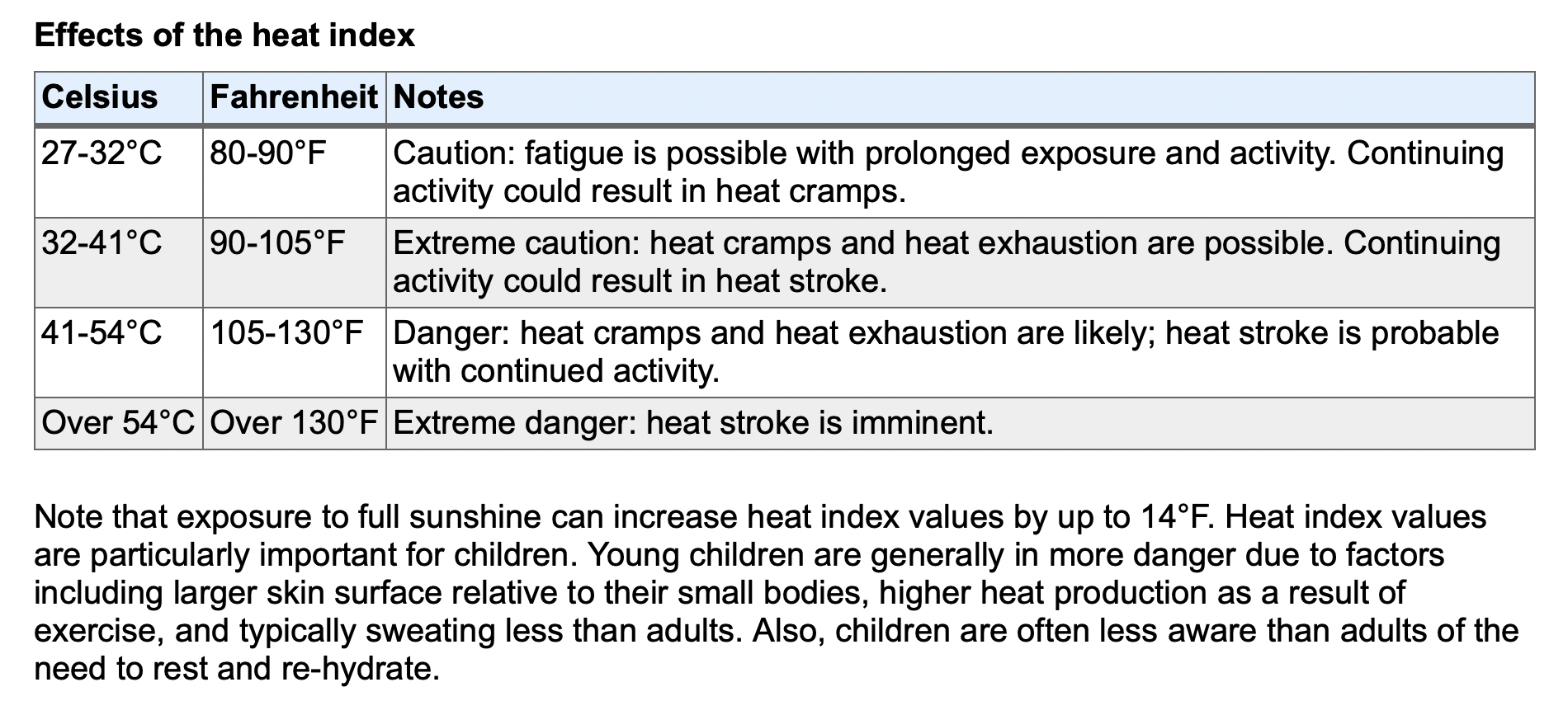
REFERENCE ARTICLES
Summer Science: Clothes Keep You Cool, More Or Less
https://www.npr.org/2012/07/25/157302810/summer-science-clothes-keep-you-cool-more-or-less
Think light and loose. That's because even if you don't feel
like you're sweating, you still want to evaporate moisture
off your skin. The loose clothing allows air to pass long
the skin and exit, speeding evaporation and carrying off
excess heat.
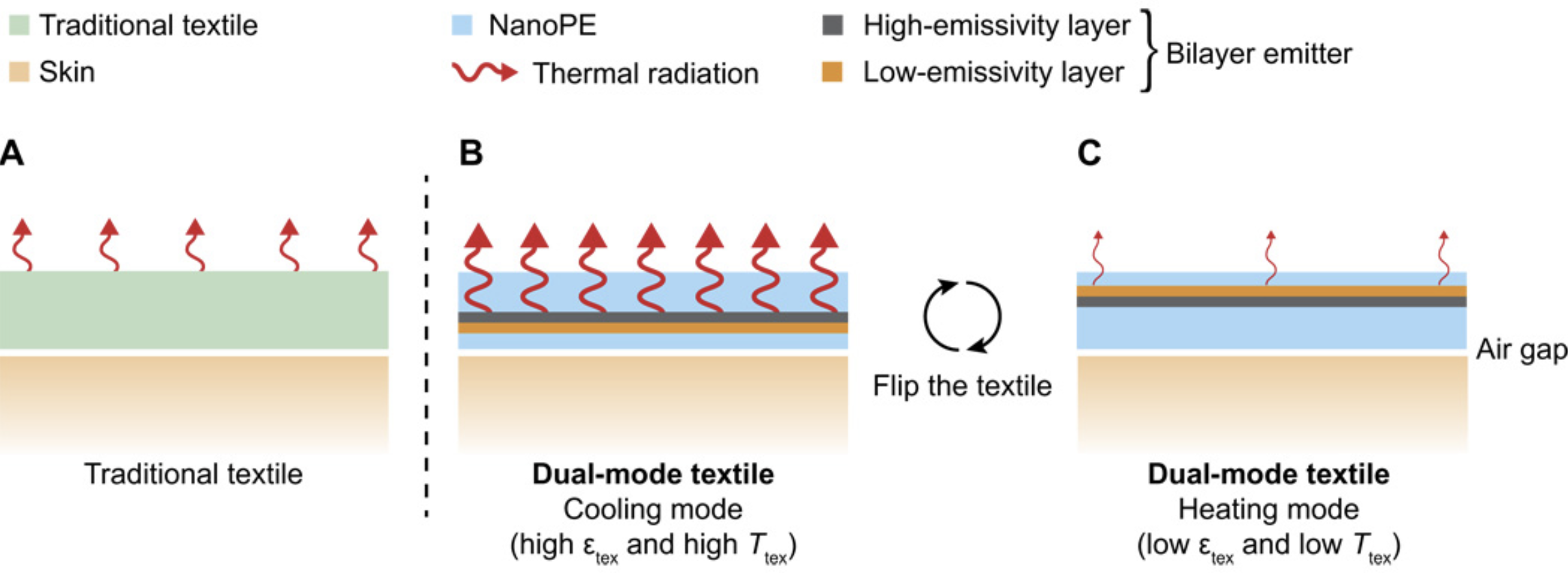
A dual-mode textile for human body radiative heating and
cooling
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.1700895
The dual-mode textile is composed of a bilayer emitter
embedded inside an infrared-transparent nanoporous
polyethylene (nanoPE) layer. We demonstrate that the
asymmetrical characteristics of both emissivity and nanoPE
thickness can result in two different heat transfer
coefficients and achieve heating when the low-emissivity
layer is facing outside and cooling by wearing the textile
inside out when the high-emissivity layer is facing outside.
This can expand the thermal comfort zone by 6.5°C (11.7°F).
Numerical fitting of the data further predicts 14.7°C
(26.5°F) of comfort zone expansion for dual-mode
textiles with large emissivity contrast.
 Other Weather Resources
http://edu-observatory.org/ipod-weather.html#HEAT
sam.wormley@icloud.com
Other Weather Resources
http://edu-observatory.org/ipod-weather.html#HEAT
sam.wormley@icloud.com

Attractive intermolecular forces are categorized into the following types: o Hydrogen bonding o Ion-dipole forces and ion-induced dipole forces o Van der Waals forces Two important principles: 1. Evaporation: Cools the Water ==> Warms the Atmosphere 2. No evaporation takes place when the relative humidity of the air is 100 percent (saturated)
EXTREMELY HOT, HUMID WEATHER COULD KILL A PERSON FAR MORE EASILY THAN WE THOUGHT https://www.sciencealert.com/human-survival-in-hot-and-humid-conditions-is https://www.sciencealert.com/future-heat-waves-are-coming-and-these-countries-are-most-at-risk The human body might not cope with nearly as much heat and humidity as theory predicts. One of the first studies to directly assess humid heat stress among young people has found that when humidity is at an absolute max, the upper limit of human adaptability is just 31°C (87°F).
Heat Wave https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_wave https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/what-causes-a-heat-wave.html What Causes A Heat Wave? A heat wave is formed when the upper atmosphere contains high pressure which makes it stationary over a region. This stationary mass of air can remain stagnant for several days and weeks, trapping more heat and reducing convection currents. As a result, there is accumulated heat and high humidity without any precipitation or rainfall. This creates the abnormally high temperatures. Heat waves are quite common during the summer season, from May to November in the northern hemisphere. The high pressure forces air to sink to the surface of the land and acts as a barrier for heat to rise. This blankets the earth surface and traps all elements of weather without allowing them to escape. The Hazards Of A Heat Wave A heat wave is potentially more dangerous than other natural events such as hurricanes, lightning, and tornadoes. Aside from causing uncomfortably high temperatures, heat waves can result in heat illness, poor air quality, wildfires, and drought. Severe heat waves have caused catastrophic crop failures, thousands of deaths from hyperthermia, and widespread power outages due to increased use of air conditioning. A heat wave is considered extreme weather that can be a natural disaster, and a danger because heat and sunlight may overheat the human body. Heat waves can usually be detected using forecasting instruments so that a warning call can be issued. Heat Exhaustion https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_exhaustion https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/symptoms-causes/syc-20373250 Heat exhaustion is a severe form of heat illness. It is a medical emergency. Heat exhaustion is caused by the loss of water and electrolytes through sweating. Heat Stroke https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_stroke https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20353581 Heatstroke is a condition caused by your body overheating, usually as a result of prolonged exposure to or physical exertion in high temperatures. This most serious form of heat injury, heatstroke, can occur if your body temperature rises to 104°F (40°C) or higher. The condition is most common in the summer months and heat waves. Heatstroke requires emergency treatment. Untreated heatstroke can quickly damage your brain, heart, kidneys and muscles. The damage worsens the longer treatment is delayed, increasing your risk of serious complications or death.



Mayo Clinic - Heat Exhaustion https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373253

Mayo Clinic - Heat Stroke https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20353581

How to protect the people you care about from extreme heat https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2022/08/04/1114996392/how-to-protect-the-people-you-care-about-from-extreme-heat https://www.npr.org/2022/07/01/1109415329/how-to-stay-safe-and-cool-in-extreme-heat
How to Keep Cool When You Don't Have Air Conditioning at Home https://www.ecowatch.com/staying-cool-tips-heat-climate-change.html
Evaporative Cooling (won't work in high humidity) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Passive_cooling https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evaporative_cooler Cooling air temperatures that can be achieved by a direct evaporative cooler at various outdoor conditions.
IMPORTANT: If power fails, there is no air conditioning, no fans, water may become scarce or may not be cool enough to cool your body. The only thing that can cool you is something colder than the human body, preferably cooler than ~84°F. Water running through underground pipes will tend to be cooled (or heated) to the subsurface soil temperature. These soil depth temperatures (below) are updated daily. Soil Temperatures (US) Often Affects Tap Water Temperature https://www.greencastonline.com/tools/soil-temperature
Graphic Watches, Warnings or Advisories (CONUS) https://www.weather.gov Watches, Warnings or Advisories (Iowa) https://www.weather.gov/dmx/ Text Watches, Warnings or Advisories for the United States https://alerts.weather.gov/cap/us.php?x=1 Watches, Warnings or Advisories by State http://edu-observatory.org/olli/HEAT/warn_by_state.html Watches and Warnings (Iowa) https://alerts.weather.gov/cap/ia.php?x=1 HeatRisk Advisory Watch Warning MesoscaleAnalysis AQI Drought Risk
Air Sea HeatIndexForecast Check IA Ames Watch Warning Outages
IMPORTANT: One of the reasons heat can be so dangerous is because people don't take the risk seriously. It surprises many people to learn that the heat index values in the chart above are for shady locations. If you are exposed to direct sunlight, the heat index value can be increased by up to 14°F. Heat indices meeting or exceeding 103°F can lead to dangerous heat disorders with prolonged exposure and/or physical activity in the heat.

Other Weather Resources http://edu-observatory.org/ipod-weather.html#HEAT sam.wormley@icloud.com