RADIATION
 BACKGROUND RADIATION
BACKGROUND RADIATION
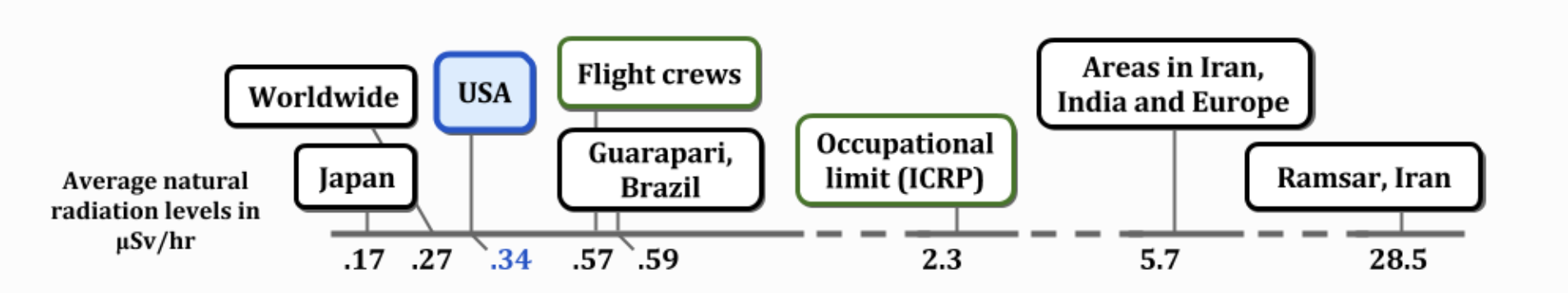 0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr
RADIATION SOURCES
0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr
RADIATION SOURCES

 Potassium-40 (K-40) is a naturally occurring radioactive
isotope of potassium with a half-life of approximately 1.25
billion years. It undergoes decay via beta emission and
electron capture, producing argon-40 and calcium-40. As one
of the primary sources of natural radioactivity, K-40
contributes to background radiation and is present in trace
amounts in all potassium-containing materials.
Potassium-40 is found in nature as a small fraction of
natural potassium, present in soils, rocks, and oceans. It
is also found in food sources rich in potassium, such as
bananas, potatoes, and certain nuts, making it an integral
part of the human diet and environment. Despite its
radioactivity, the levels of K-40 in natural settings are
low and pose no significant health risk.
RADIATION SOURCES IN THE CONTEXT OF A WARMING PLANET
Potassium-40 (K-40) is a naturally occurring radioactive
isotope of potassium with a half-life of approximately 1.25
billion years. It undergoes decay via beta emission and
electron capture, producing argon-40 and calcium-40. As one
of the primary sources of natural radioactivity, K-40
contributes to background radiation and is present in trace
amounts in all potassium-containing materials.
Potassium-40 is found in nature as a small fraction of
natural potassium, present in soils, rocks, and oceans. It
is also found in food sources rich in potassium, such as
bananas, potatoes, and certain nuts, making it an integral
part of the human diet and environment. Despite its
radioactivity, the levels of K-40 in natural settings are
low and pose no significant health risk.
RADIATION SOURCES IN THE CONTEXT OF A WARMING PLANET

 Radon-222 (Rn-222) occurs naturally - part of the uranium-238
decay chain. It is found in soil, rocks, and groundwater in
areas with high uranium or radium content. It can
accumulate in enclosed spaces like basements and buildings,
where it is a significant contributor to natural background
radiation. High levels of radon in homes and workplaces are
considered a health hazard due to its radioactive decay
products, which can attach to dust particles and be
inhaled. Monitoring and mitigation measures are often
implemented in regions with elevated radon levels to
minimize health risks.
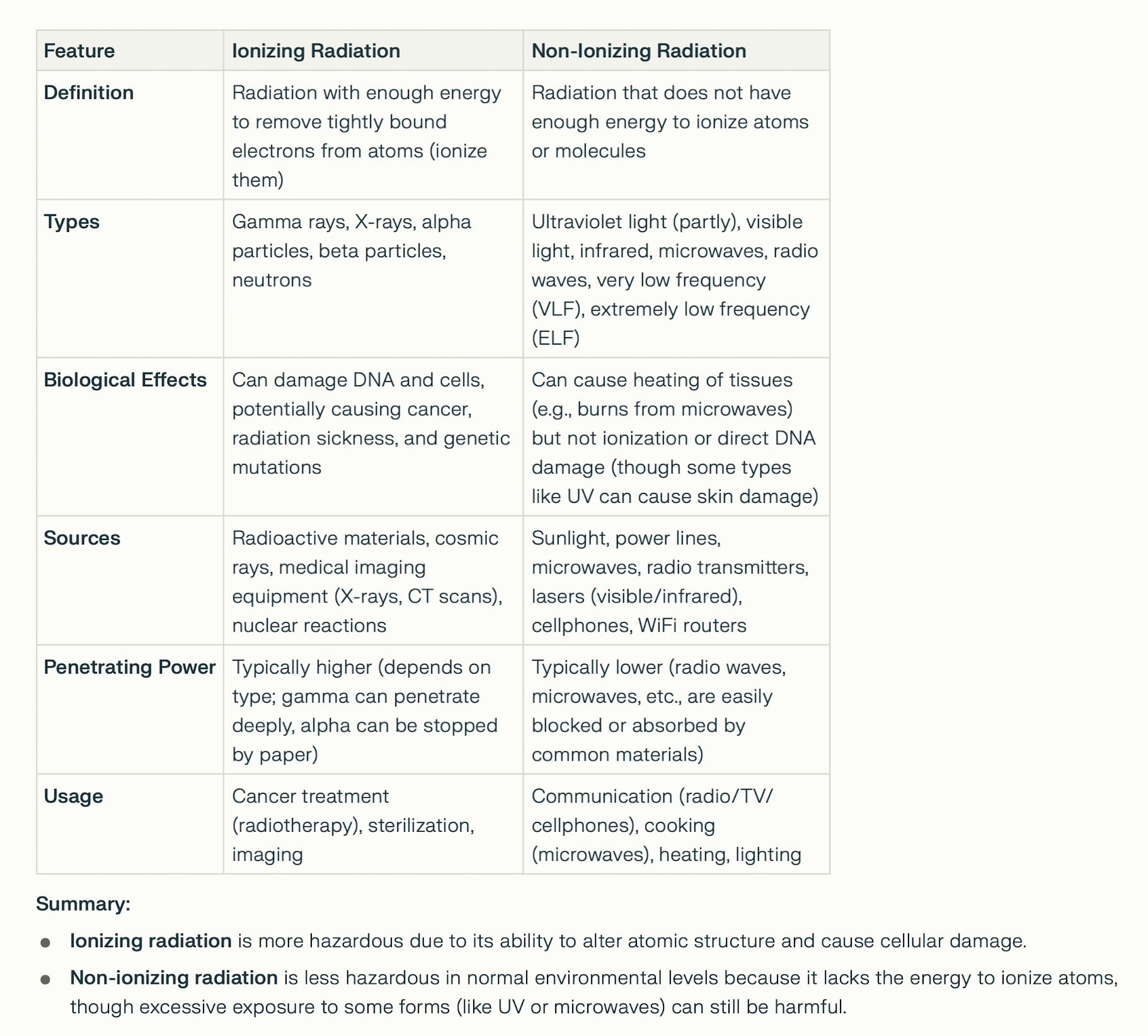
IONIZING RADIATION
Radon-222 (Rn-222) occurs naturally - part of the uranium-238
decay chain. It is found in soil, rocks, and groundwater in
areas with high uranium or radium content. It can
accumulate in enclosed spaces like basements and buildings,
where it is a significant contributor to natural background
radiation. High levels of radon in homes and workplaces are
considered a health hazard due to its radioactive decay
products, which can attach to dust particles and be
inhaled. Monitoring and mitigation measures are often
implemented in regions with elevated radon levels to
minimize health risks.
IONIZING RADIATION
 MRI vs CT RADIATION
MRI vs CT RADIATION
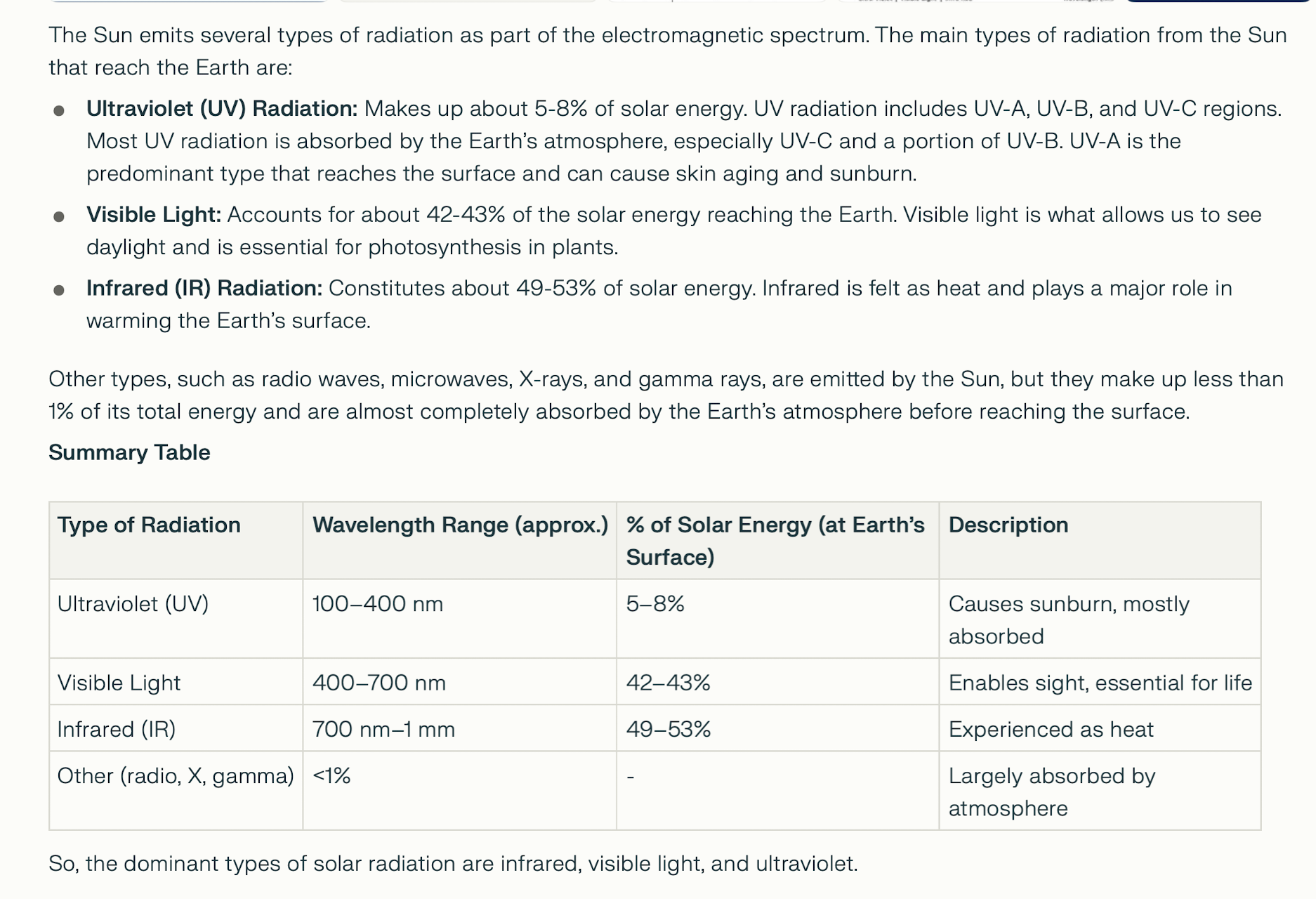
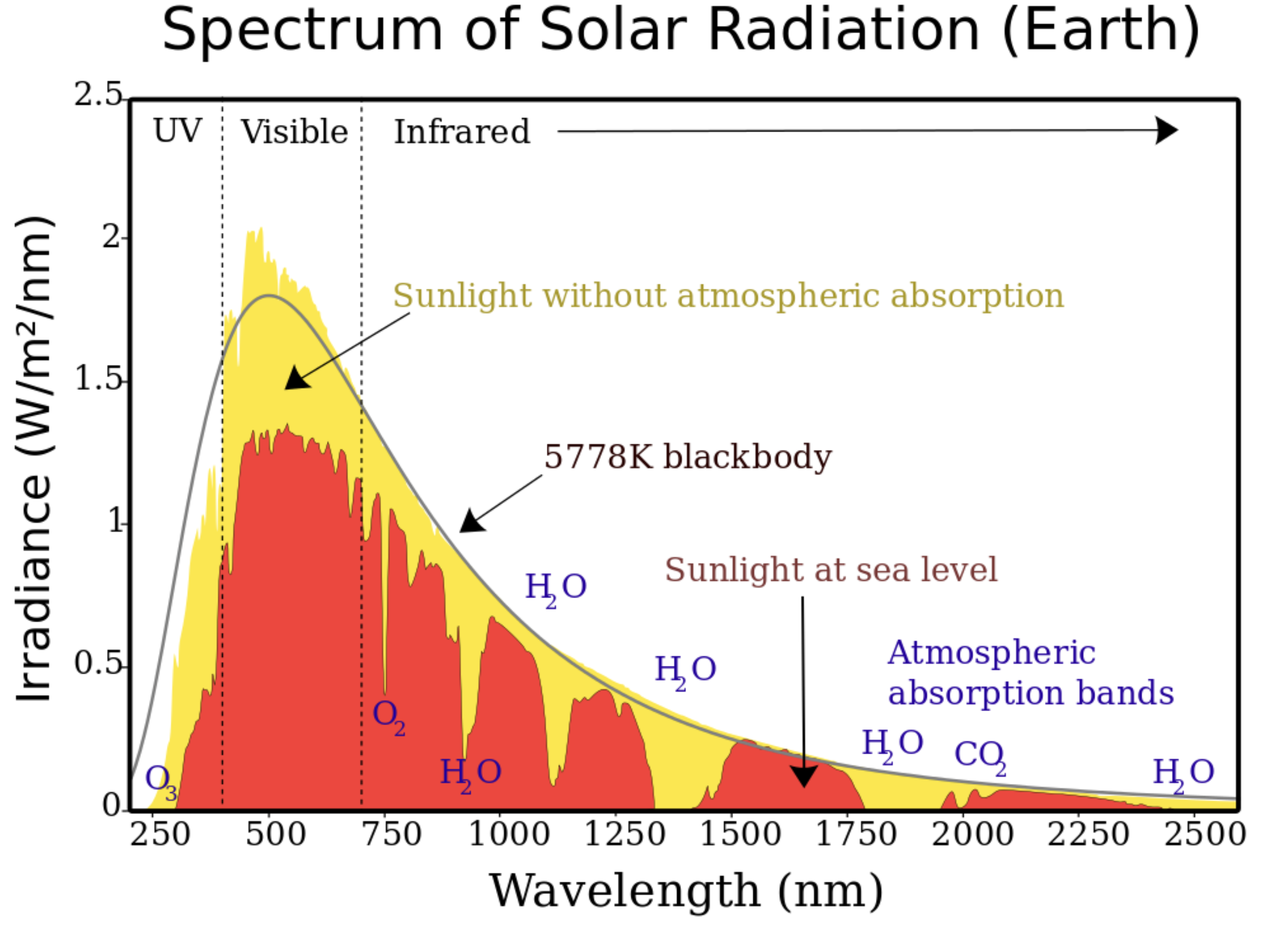
 SOLAR RADIATION
SOLAR RADIATION
 SOLAR WIND
SOLAR WIND
 Solar Flare
Solar Flare
 GEOMAGNETIC STORMS
GEOMAGNETIC STORMS
 GEOMAGNETIC STORMS
GEOMAGNETIC STORMS
 RADIACODE 103G GAMMA SCINTILLATOR REVIEW
RADIACODE 103G GAMMA SCINTILLATOR REVIEW 
 Gadolinium Aluminum Gallium Garnet (GAGG:Ce)
RADIACODE LIBRARY REVIEW
Gadolinium Aluminum Gallium Garnet (GAGG:Ce)
RADIACODE LIBRARY REVIEW
 RADIACODE 103G DOSE RATE CALIBRATION MORE ABOUT DOSE
RADIACODE 103G DOSE RATE CALIBRATION MORE ABOUT DOSE
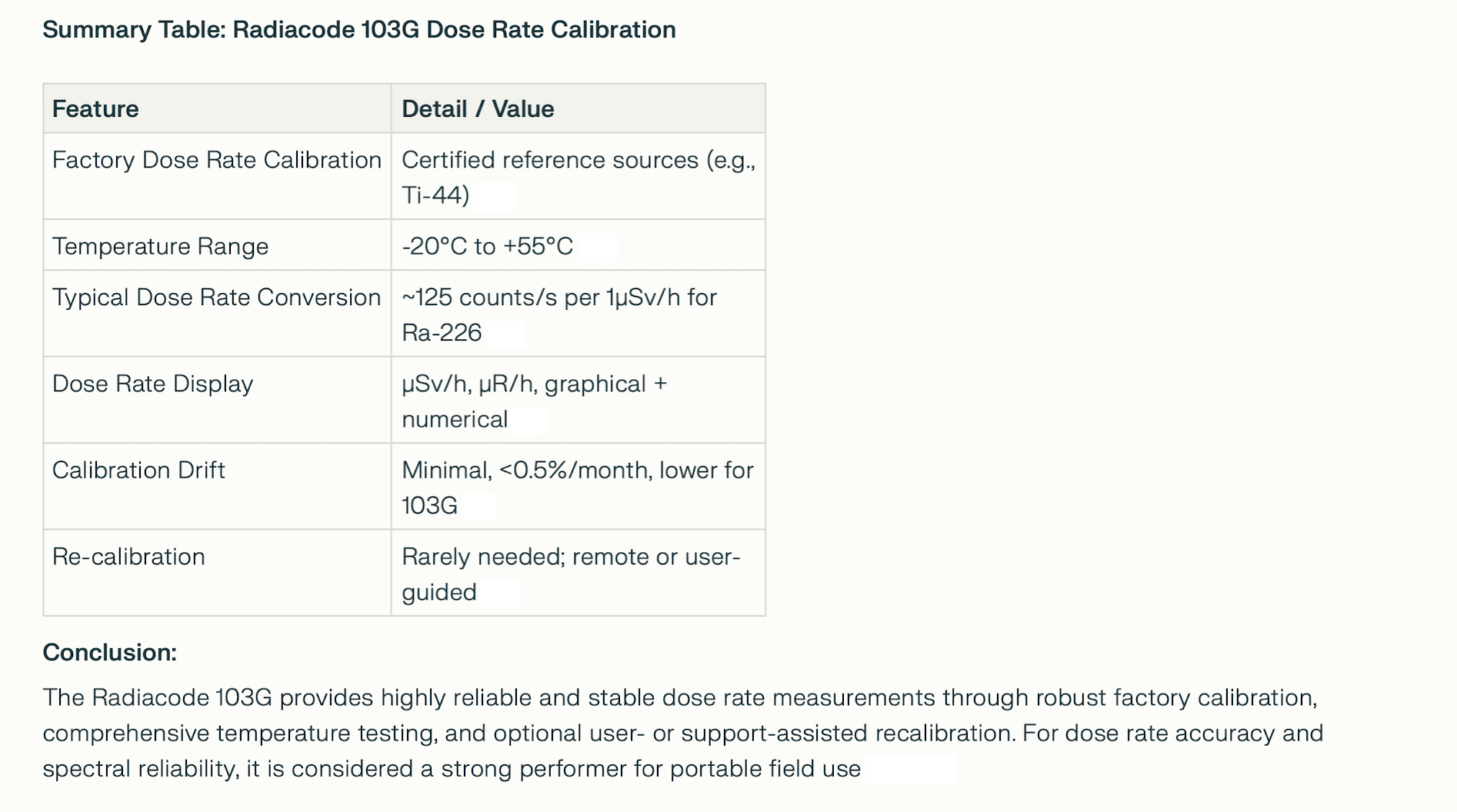
 DOSE RATE CALIBRATION SUMMARY MORE ABOUT DOSE
DOSE RATE CALIBRATION SUMMARY MORE ABOUT DOSE
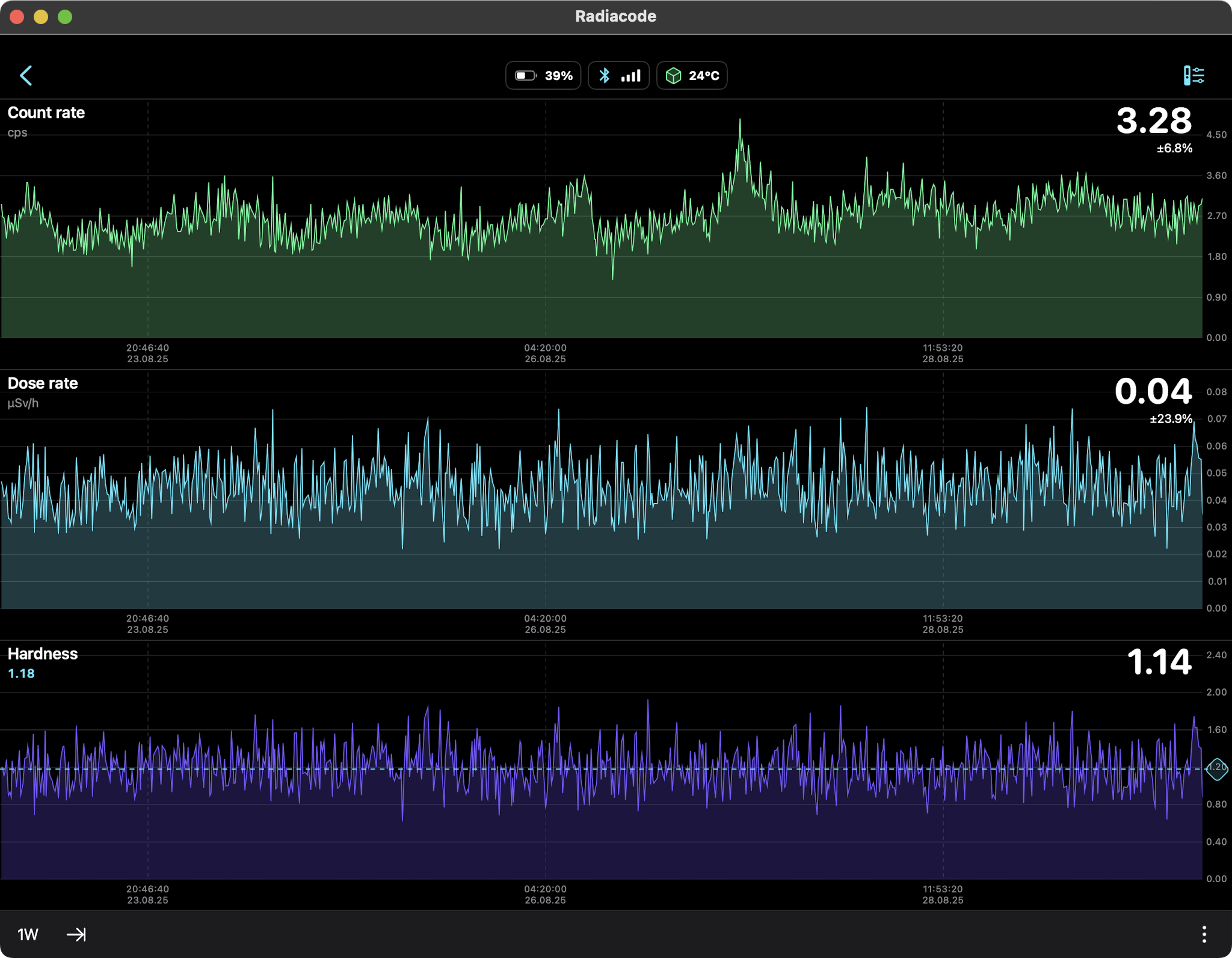
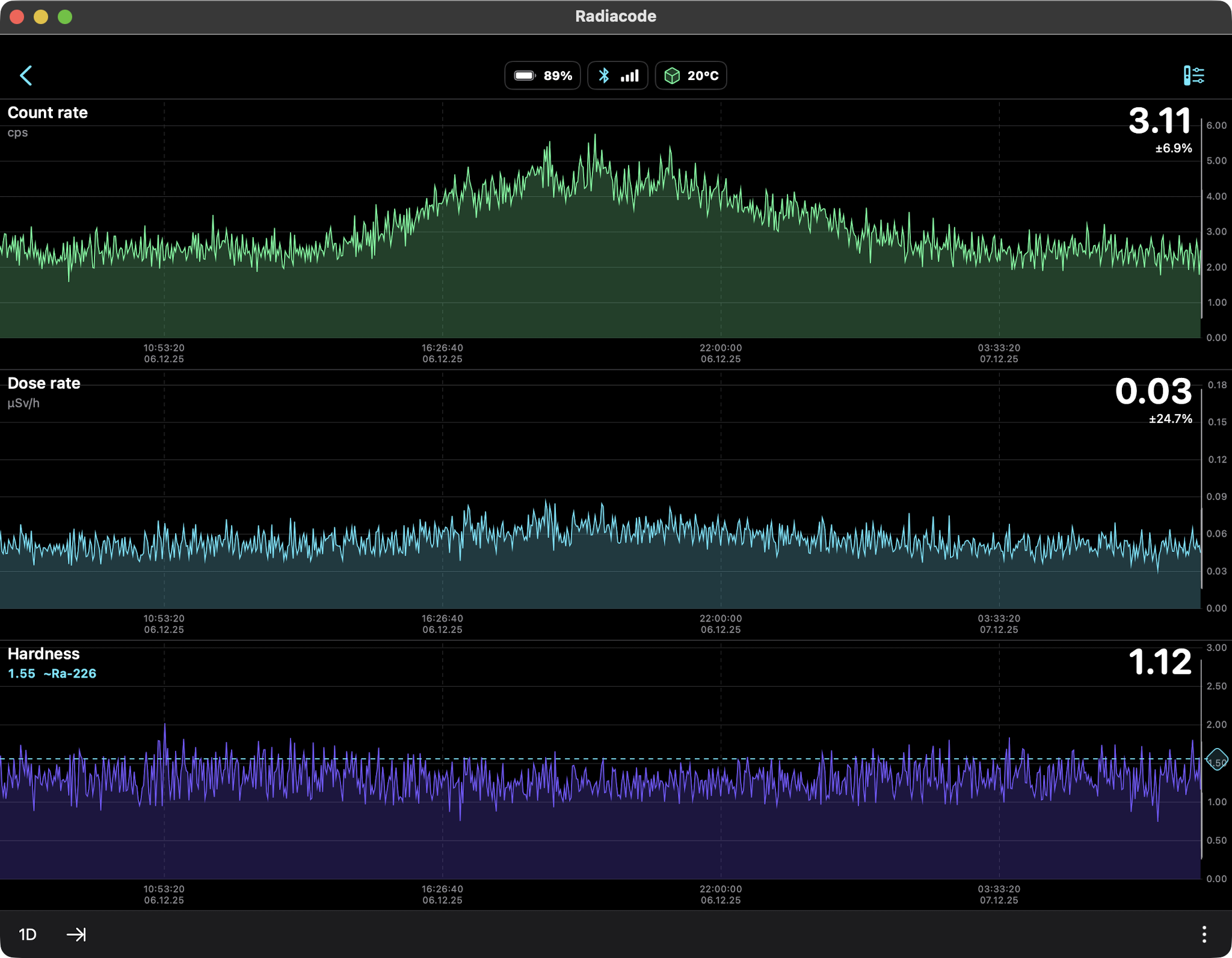
 DIURNAL RADIATION PATTERNS FROM RADON
DIURNAL RADIATION PATTERNS FROM RADON
 Seven days of background radiation
Seven days of background radiation
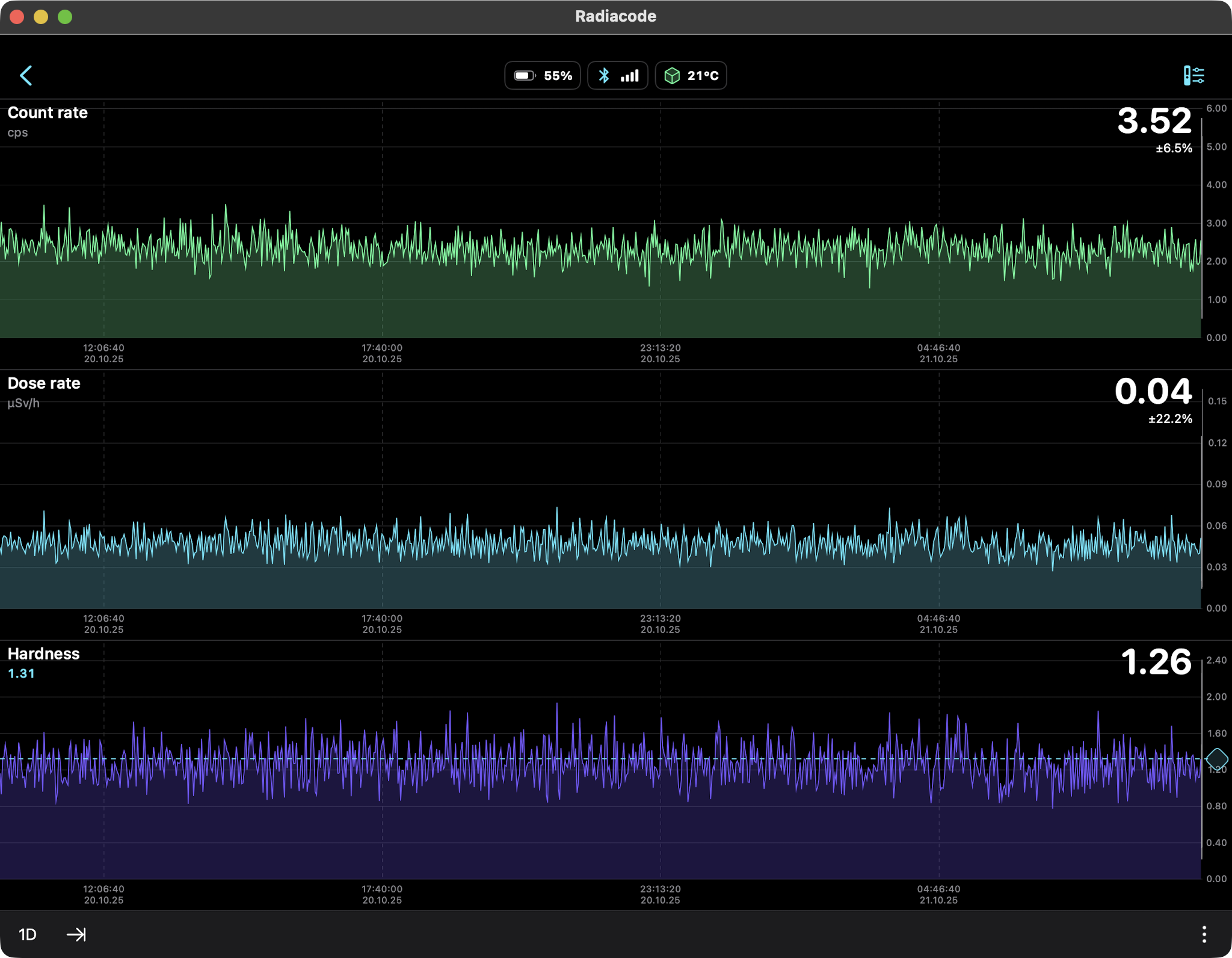
 0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr
But when it's Windy, the background radiation is Calm
0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr
But when it's Windy, the background radiation is Calm
 GAMMA RADIATION FROM RAIN STORMS
GAMMA RADIATION FROM RAIN STORMS
 Lightning and Rain (two separate thunder storms) 24hr
Lightning and Rain (two separate thunder storms) 24hr
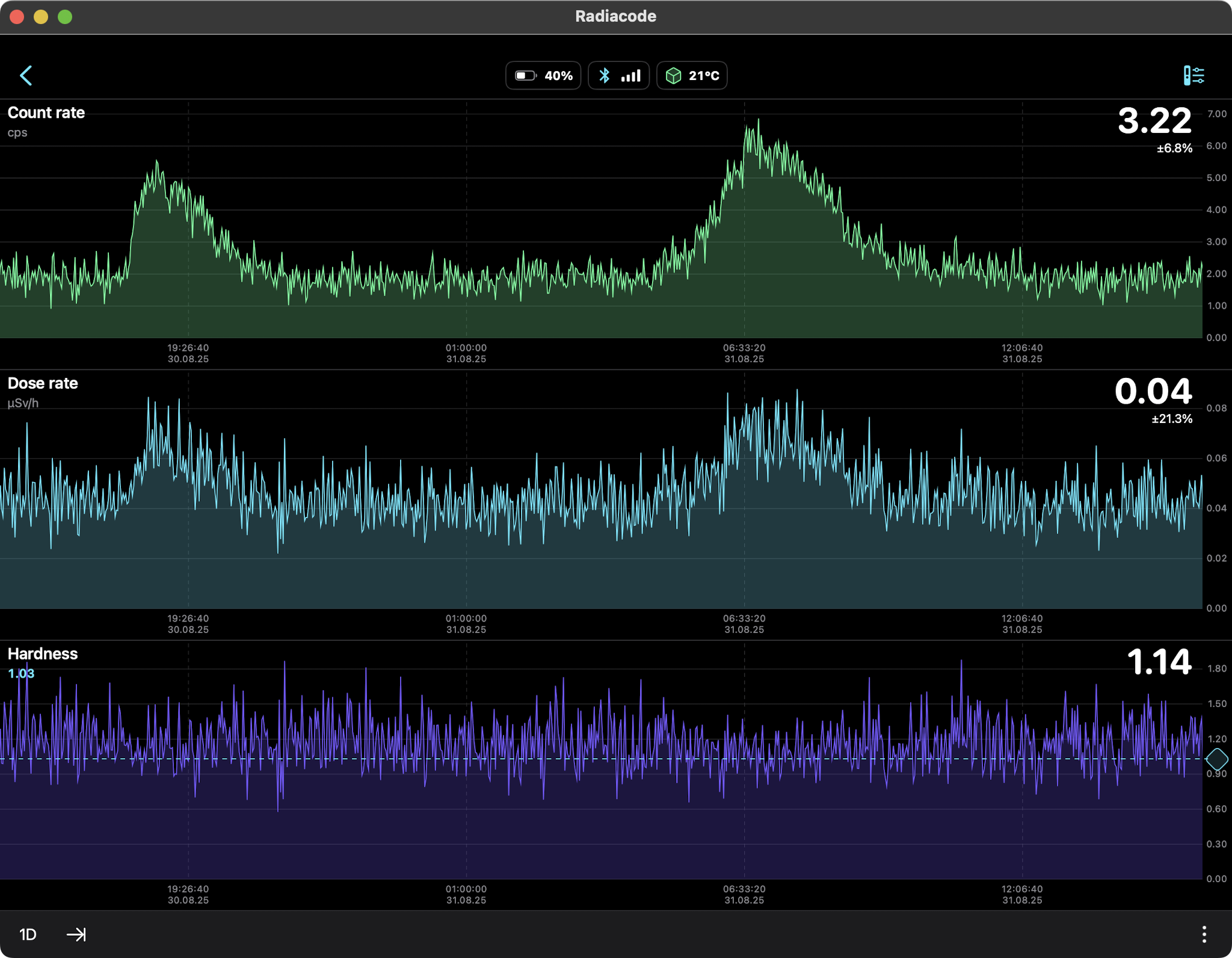 Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
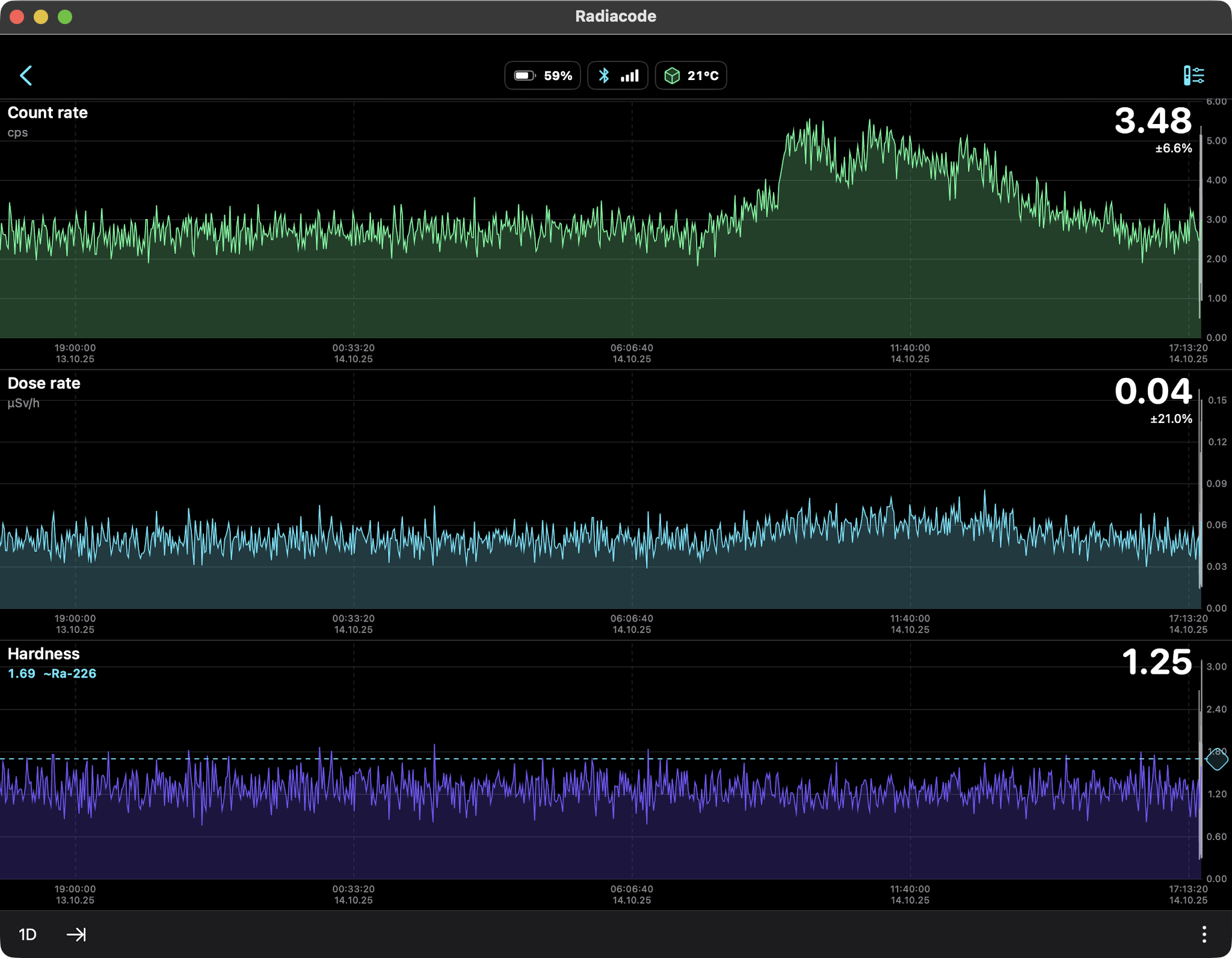 Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
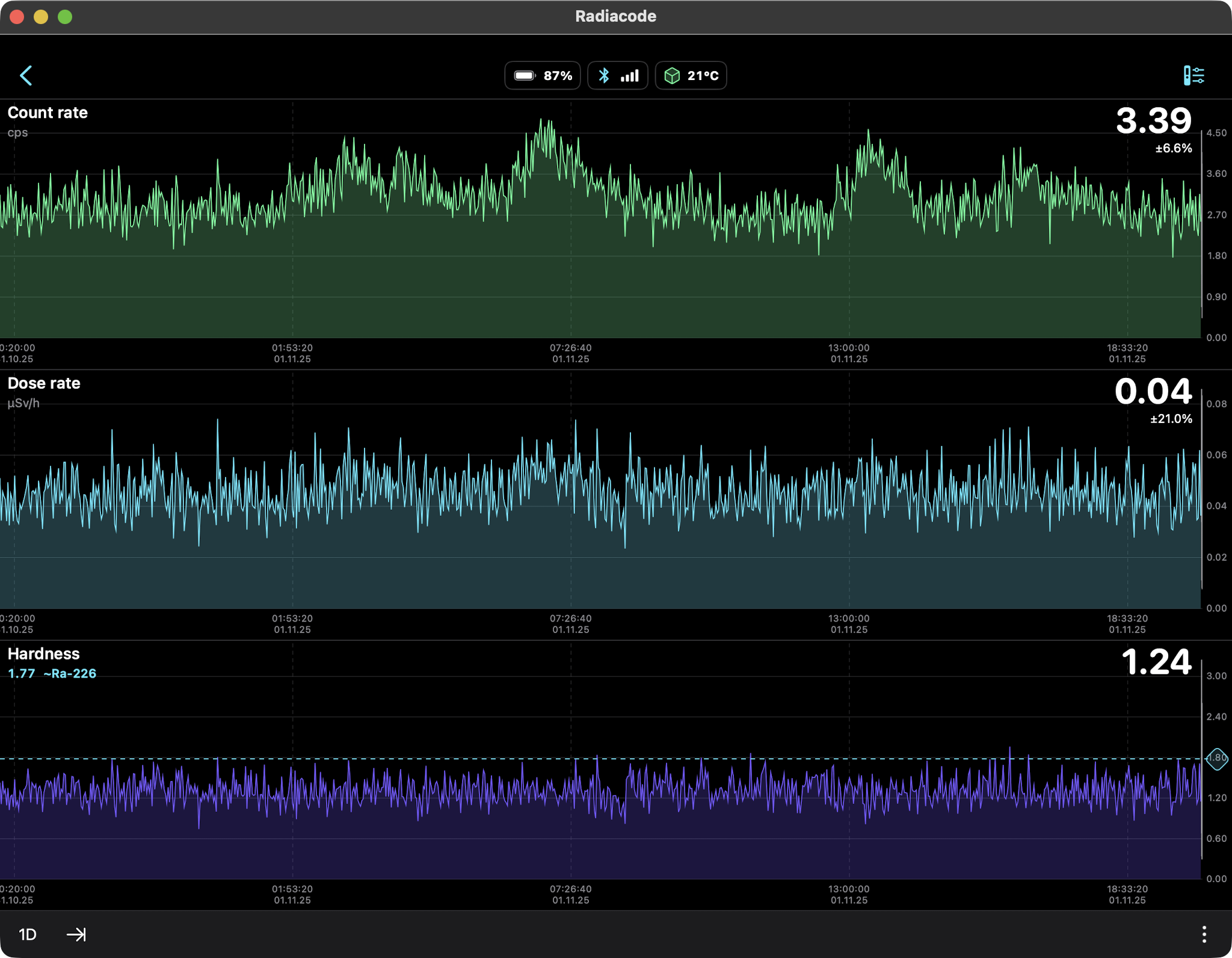 Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
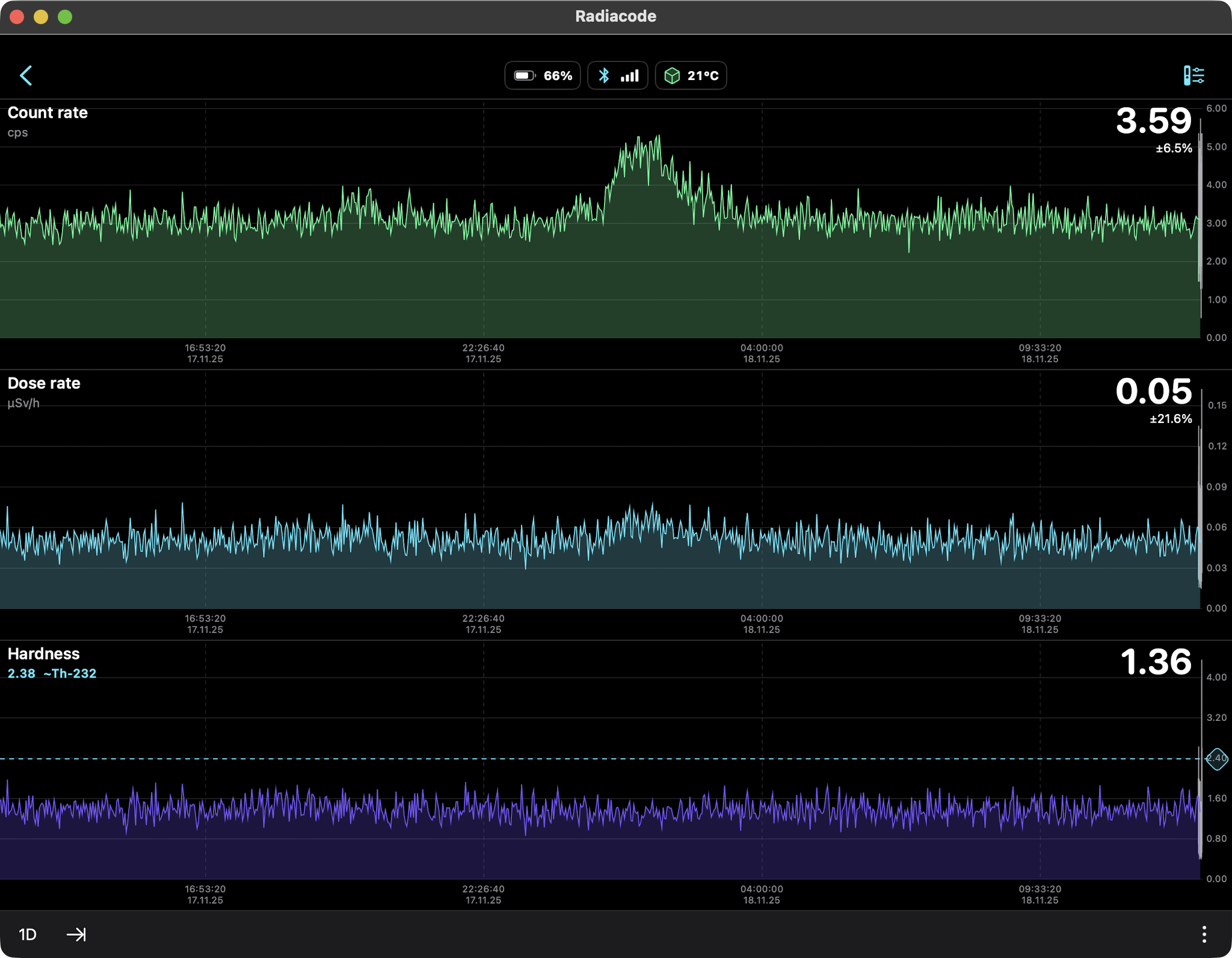 Snow Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
Snow Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
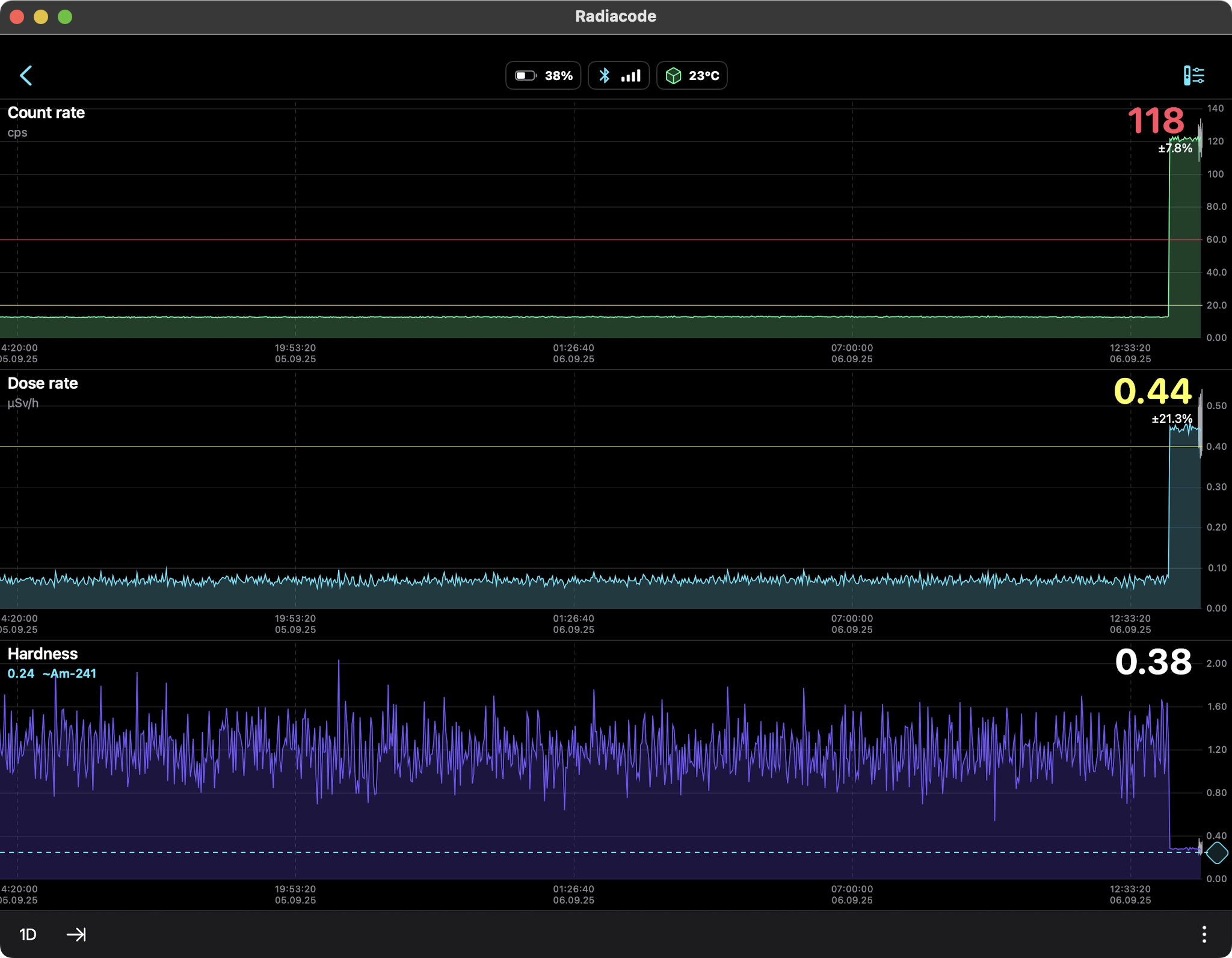
 AMERICIUM-241 (USED IN MOST SMOKE DETECTORS)
AMERICIUM-241 (USED IN MOST SMOKE DETECTORS)
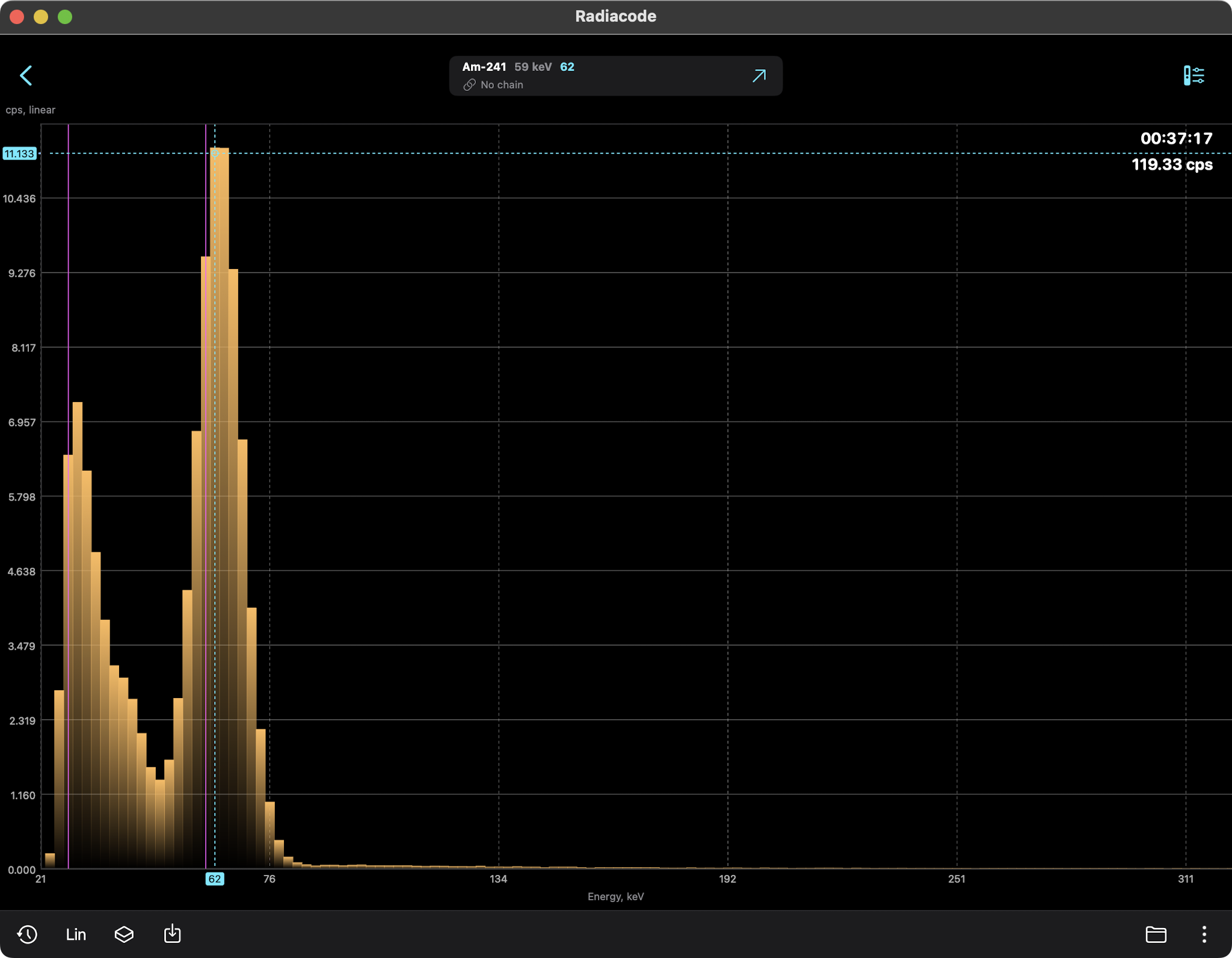 Americium-241 (Am-241) is a radioactive isotope of
americium with a half-life of approximately 432.2 years. It
primarily undergoes alpha decay, emitting alpha particles
and low-energy gamma radiation. Am-241 is a byproduct of
plutonium-241 decay, typically produced in nuclear reactors
during the operation of nuclear fuel cycles. Its alpha
decay is accompanied by gamma radiation, which makes it
useful for a variety of applications.
Americium-241 is an alpha particle emitter, often used
in smoke detectors. The alpha particles do not escape their
containers. Note, however, that any nucleus undergoing
radioactive decay also emits weak gamma and x-ray photons
and is often detectable with gamma ray scintillators.
Americium-241 (Am-241) is a radioactive isotope of
americium with a half-life of approximately 432.2 years. It
primarily undergoes alpha decay, emitting alpha particles
and low-energy gamma radiation. Am-241 is a byproduct of
plutonium-241 decay, typically produced in nuclear reactors
during the operation of nuclear fuel cycles. Its alpha
decay is accompanied by gamma radiation, which makes it
useful for a variety of applications.
Americium-241 is an alpha particle emitter, often used
in smoke detectors. The alpha particles do not escape their
containers. Note, however, that any nucleus undergoing
radioactive decay also emits weak gamma and x-ray photons
and is often detectable with gamma ray scintillators.
 0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr
So should we be concerned about this radiation source? Not
really. The weak gamma and x-ray emissions fall off as the
square of the distance so they are literally undetectable
several feet away. At just one centimeter from the source
the Radiacode 103G measured a dose rate of 0.44 µSv/h which
is slightly higher than the US average background level of
0.34 µSv/hr. No concern, as we are much further away than a
centimeter.
0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr
So should we be concerned about this radiation source? Not
really. The weak gamma and x-ray emissions fall off as the
square of the distance so they are literally undetectable
several feet away. At just one centimeter from the source
the Radiacode 103G measured a dose rate of 0.44 µSv/h which
is slightly higher than the US average background level of
0.34 µSv/hr. No concern, as we are much further away than a
centimeter.
 sam.wormley@icloud.com
sam.wormley@icloud.com
BACKGROUND RADIATION
0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr RADIATION SOURCES

Potassium-40 (K-40) is a naturally occurring radioactive isotope of potassium with a half-life of approximately 1.25 billion years. It undergoes decay via beta emission and electron capture, producing argon-40 and calcium-40. As one of the primary sources of natural radioactivity, K-40 contributes to background radiation and is present in trace amounts in all potassium-containing materials. Potassium-40 is found in nature as a small fraction of natural potassium, present in soils, rocks, and oceans. It is also found in food sources rich in potassium, such as bananas, potatoes, and certain nuts, making it an integral part of the human diet and environment. Despite its radioactivity, the levels of K-40 in natural settings are low and pose no significant health risk. RADIATION SOURCES IN THE CONTEXT OF A WARMING PLANET

Radon-222 (Rn-222) occurs naturally - part of the uranium-238 decay chain. It is found in soil, rocks, and groundwater in areas with high uranium or radium content. It can accumulate in enclosed spaces like basements and buildings, where it is a significant contributor to natural background radiation. High levels of radon in homes and workplaces are considered a health hazard due to its radioactive decay products, which can attach to dust particles and be inhaled. Monitoring and mitigation measures are often implemented in regions with elevated radon levels to minimize health risks. IONIZING RADIATION
MRI vs CT RADIATION
SOLAR RADIATION

SOLAR WIND
Solar Flare
GEOMAGNETIC STORMS
GEOMAGNETIC STORMS
RADIACODE 103G GAMMA SCINTILLATOR REVIEW

Gadolinium Aluminum Gallium Garnet (GAGG:Ce) RADIACODE LIBRARY REVIEW
RADIACODE 103G DOSE RATE CALIBRATION MORE ABOUT DOSE
DOSE RATE CALIBRATION SUMMARY MORE ABOUT DOSE
DIURNAL RADIATION PATTERNS FROM RADON
Seven days of background radiation

0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr But when it's Windy, the background radiation is Calm
GAMMA RADIATION FROM RAIN STORMS
Lightning and Rain (two separate thunder storms) 24hr
Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
Rain Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
Snow Only (Radon daughters Pb-214, Bi-214) 24hr
AMERICIUM-241 (USED IN MOST SMOKE DETECTORS)

Americium-241 (Am-241) is a radioactive isotope of americium with a half-life of approximately 432.2 years. It primarily undergoes alpha decay, emitting alpha particles and low-energy gamma radiation. Am-241 is a byproduct of plutonium-241 decay, typically produced in nuclear reactors during the operation of nuclear fuel cycles. Its alpha decay is accompanied by gamma radiation, which makes it useful for a variety of applications. Americium-241 is an alpha particle emitter, often used in smoke detectors. The alpha particles do not escape their containers. Note, however, that any nucleus undergoing radioactive decay also emits weak gamma and x-ray photons and is often detectable with gamma ray scintillators.
0.34 µSv/hr equals 2.98 mSv/yr So should we be concerned about this radiation source? Not really. The weak gamma and x-ray emissions fall off as the square of the distance so they are literally undetectable several feet away. At just one centimeter from the source the Radiacode 103G measured a dose rate of 0.44 µSv/h which is slightly higher than the US average background level of 0.34 µSv/hr. No concern, as we are much further away than a centimeter.

sam.wormley@icloud.com